Water supply to objects is carried out by a number of mechanisms and structures: pumping stations, pipelines, filtration stations, water intakes. The coordinated work of all components increases the efficiency and reliability of the systems, reduces energy consumption and improves the final water performance. For the coordination of individual units, automated water supply and sewerage systems are equipped.
Requirements for automatic water supply installations

Modern technologies make it possible to automate almost any water supply system:
- artesian women;
- filtering stations;
- sewer pumping stations;
- stations of the first and second ascents;
- booster stations;
- treatment facilities.
It must be borne in mind that the process of extraction, purification and delivery of water is associated with a variety of physical, chemical and biological reactions. Automation of the water supply process is carried out taking into account the following features:
- the intensity of the equipment is constantly changing;
- the characteristics of the primary water are not stable;
- the equipment is located at separate points from each other, they are controlled from a single center;
- strict requirements for the quality of water supplied to the consumer;
- work in economy mode;
- in case of a breakdown in one area, ensuring the operation of the rest of the equipment in normal mode.
Complete set of automated water supply system

Automation of the water supply process is carried out using:
- measuring transducers;
- sensors for measuring indicators and, water consumption;
- data input and output blocks;
- executive mechanisms;
- controller.
Sensors define characteristics, regulate and signal problems in processes.
Input and output modules (blocks) translate the information received from the sensors into a format convenient for processing and deliver it further to the controller.
Measuring transducers transform the controlled parameters or signals into a form convenient for storage or processing.
Controller controls technological processes using sensor data. Unlike consumer computers, industrial controllers are equipped with a powerful system for input and output of signals from the periphery. They do not require constant monitoring and can withstand adverse climatic conditions.
Actuating mechanism - receives a signal from the controller and converts it into motion. The actuator circuit for water supply automation consists of a relay, a hydraulic or pneumatic drive, and an engine.
To deliver information from the periphery to the control center, the following are used:
- radio channels;
- switch;
- mobile telephony;
- wireless Internet;
- satellite connection.
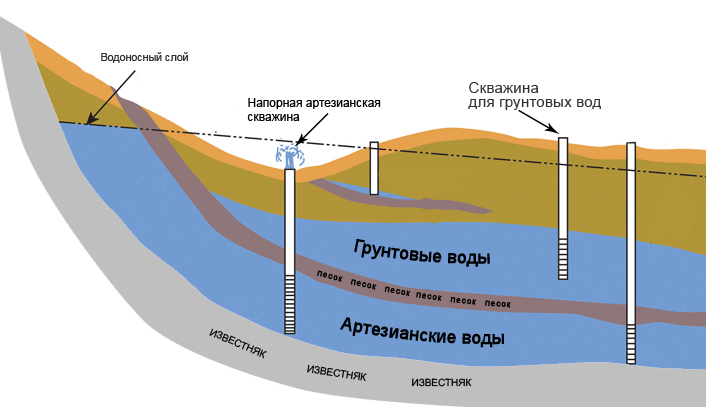
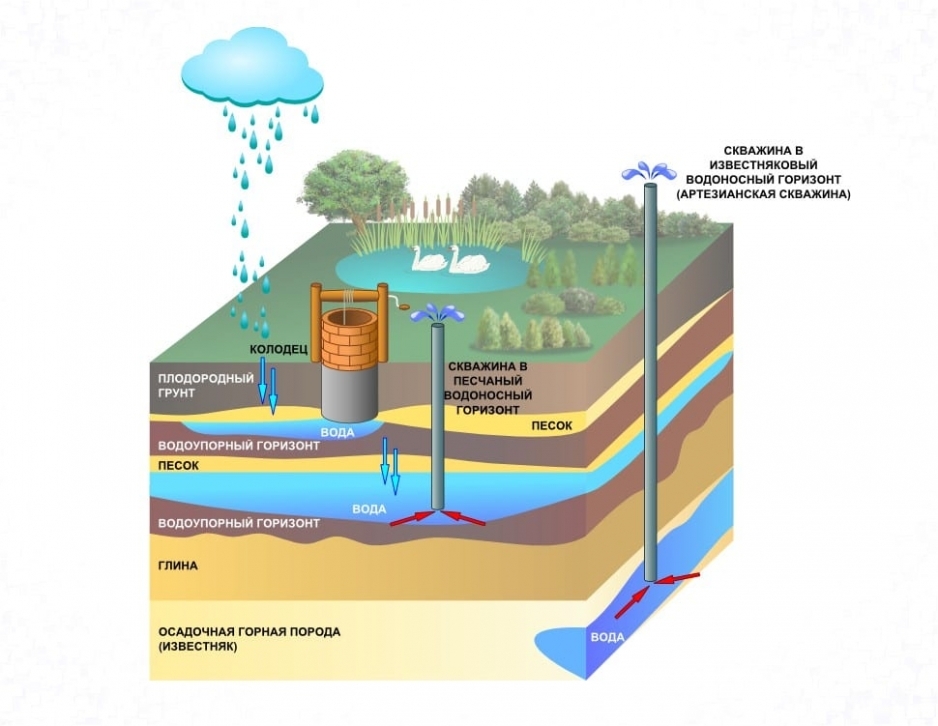
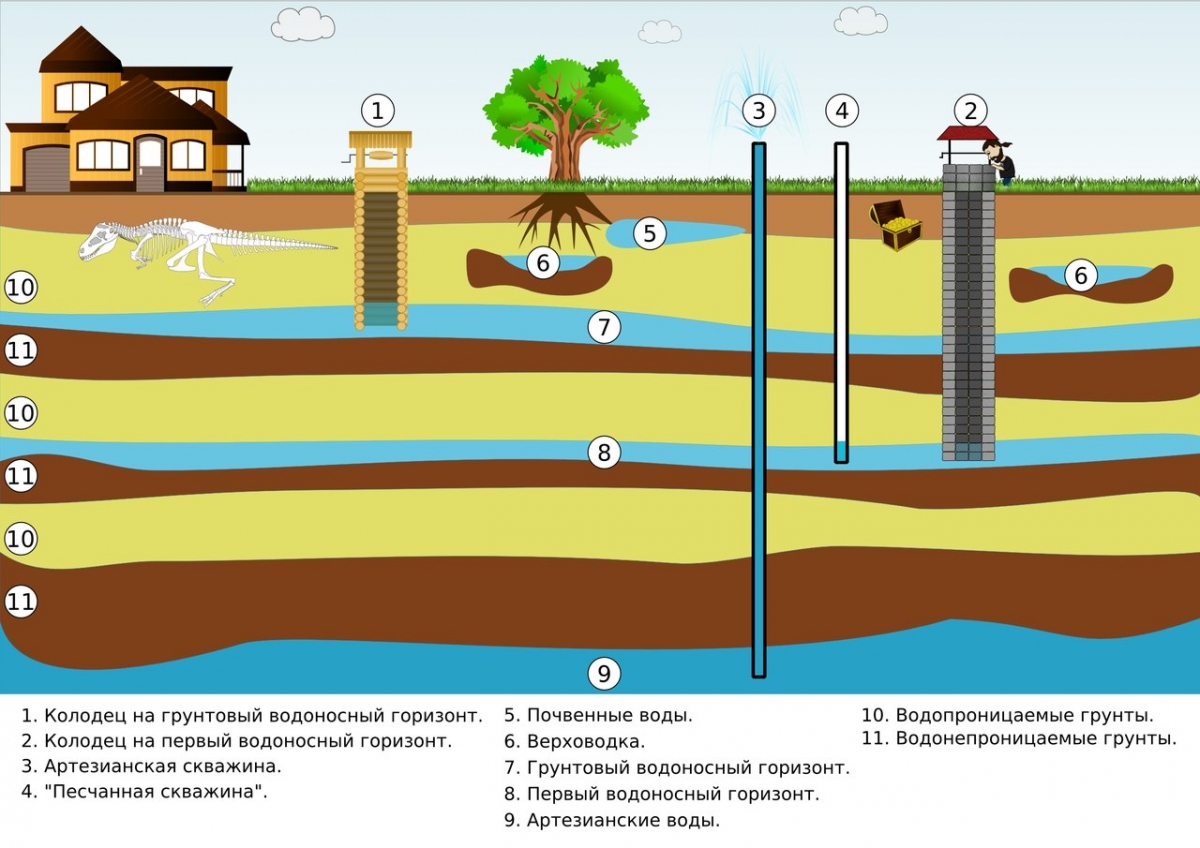
Artesian sources automation scheme
Automation of the process of water intake from deep wells and water supply to the consumer must comply with the conditions:
- the whole process from receiving water to delivery to people is automated;
- constant monitoring of water production and quantity in tanks, equipment operation is provided;
- all data are archived in the controller's databases;
- operators can change pump parameters at any time from the control room.
Water supply automation scheme
- In the control room, a panel with a controller is mounted, as well as a computer. The controller communicates with the computer wirelessly over Ethernet.
- The wells of the automated water supply and sewerage system are equipped with input and output units, sensors for monitoring voltage and pressure, pulse counters, and a soft start mechanism.
- Water intake stations are equipped with input and output units, current and pressure sensors, pulse counters. A motor protection unit is installed on each pump.
- A pressure meter is installed in the water tank.
- A twisted pair cable is used to connect all sources of water intake and stations.
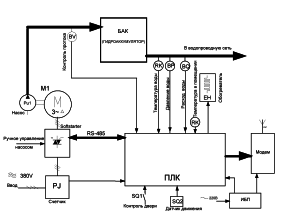
Each automated water supply and sewerage system is equipped with a control program. As a result, the pumps work without the presence of a person, maintaining the right amount of water in the tanks. They provide a predetermined pressure in the water pipes. The scheme works effectively when one pump is the leader, the other are slaves. After a certain period, the lead pump is changed, this prevents premature wear of the equipment. The automated water system controller counts the number of hours each pump has worked.
The controller analyzes equipment errors: open or short circuits in circuits, lack of communication with sensors, voltage surges, emergency limits. If the sensor breaks down, information about it comes to the control panel. In automatic mode, the controller allows the pump to run by adjusting the water flow and flow.
The operator sees on the monitor information about the break-in of equipment, flooding or fire, air temperature, water pressure and flow rate, the amount of water in the tanks. The automated water supply scheme allows the operator to remotely turn on or off the pumps, restart the smooth descent mechanism.
Water intake tower automation
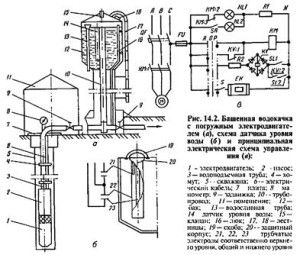
In agriculture, water supply is predominantly widespread by automated tower-type installations with submersible pumps. The control circuit of the tower pumping station makes it possible to automatically or manually turn on or off the pump, protects the electric motor from short circuits and overloads, and gives light signals about the status of the pump.
To switch water supply installations from automatic to manual mode at a tower-type pumping station, the SA toggle switch is set to P. When switched to O, the installation is turned off. When there is no water in the tower, the contacts of the sensors open, and the magnetic starter is connected. In a tower-type water supply installation, a pump automatically starts and pumps in the required amount of water. As soon as water reaches the contacts of the KV relay, the current supply to the pump is turned off. When the pump is on, the red indicator is on, when it is off, the green one.
The automated water supply system makes it possible to reduce the number of maintenance personnel, trace all processes, sensor indicators, operating modes of equipment, monitor the performance of water intake sources, and take into account the volume of produced water in real time.
Video example of automation of water supply in a village in Transbaikalia: