Water towers are found everywhere: in suburban settlements, villages, on farms, in greenhouses, in the territories of small enterprises. What are these structures, what are they for and how do they work?
What is a water tower
The first water towers were built several centuries ago. In Russia, almost the only customer for the construction of water towers for a long time was the railway, which needed voluminous reservoirs, where it would be possible to accumulate water supplies for "refueling" steam locomotives. Until now, at many stations today you can see old brick towers that have been preserved since the 19th century.
The picture has changed since 1951, when the mass construction of water towers began in the countryside, where, in fact, most of these structures are located to this day. We are talking about the so-called Rozhnovsky towers, the design of which was developed by engineer A.A. Rozhnovsky back in 1936.
This was a revolutionary technical solution. Unified economical metal towers, which are assembled in just 2 - 4 days, perform their functions without the need for winter heating of water. On the basis of Rozhnovsky's design solutions, most of the water towers were built on the territory of our country. It should be added that a significant contribution to their development was also made by engineer P.I. Zemskov.
Water towers are located all over the world. While differing in design, size and performance, they are nevertheless very similar in design and have the same functions. About this - further
Device and purpose
The main functions of the water tower
The water tower performs the following functions:
- ensuring the supply of water to consumers;
- uniform distribution of water supply with simultaneous switching on of a large number of water consumers; performing the function of a reserve source of water supply.
Varieties of water towers
- Brickwork towers (legacy method).
- Reinforced concrete.
- Reservoirs on hyperboloid supports.
- Tank on frame steel frames.
- Steel tanks of variable cross-section (Rozhnovsky towers).
- Individual tanks.
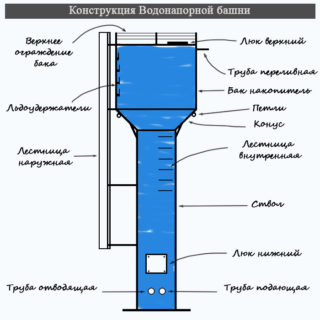
- Tank (tank) with a volume of tens to thousands of cubic meters. It is made of steel, concrete, plastic, and other anti-corrosion materials.It is set at a height based on the elevation of the tank bottom to the height of the highest consumption point.
- The support of the tank, which constitutes the main "body" of the tower up to 25 - 30 meters high. It is a monolithic or frame structure made of steel beams, reinforced concrete or bricks.
- Vertical pipeline (inlet and outlet lines). The supply pipeline supplying the tank with water is mounted from the pumps under the outer top cover of the tank. The outlet line (pipeline with a diameter of 200 mm) is connected to the water supply system.
- Ventilation hatch. Located at the top of the tank and designed to maintain pressure when the water supply is cut off.
- Pump equipment. Placed in a free-standing structure built over a water supply source. Equipped with a control system that periodically turns on the pumps to pump water in case of a drop in water level.
- Filtration system.
Principle of operation
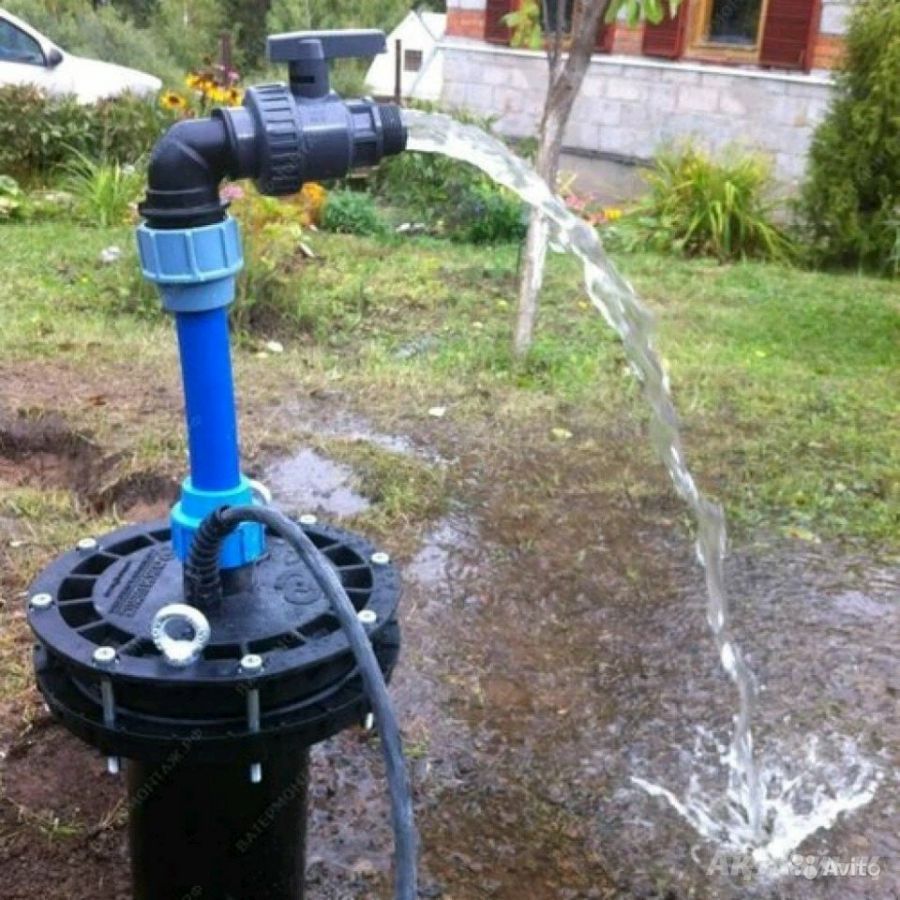
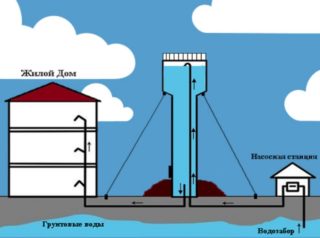
- water from a water supply source is pumped through a pipeline into a storage tank;
- from the tank, water under the pressure created by the difference in the height of the location of the tank and the level of the water supply system enters the water supply network;
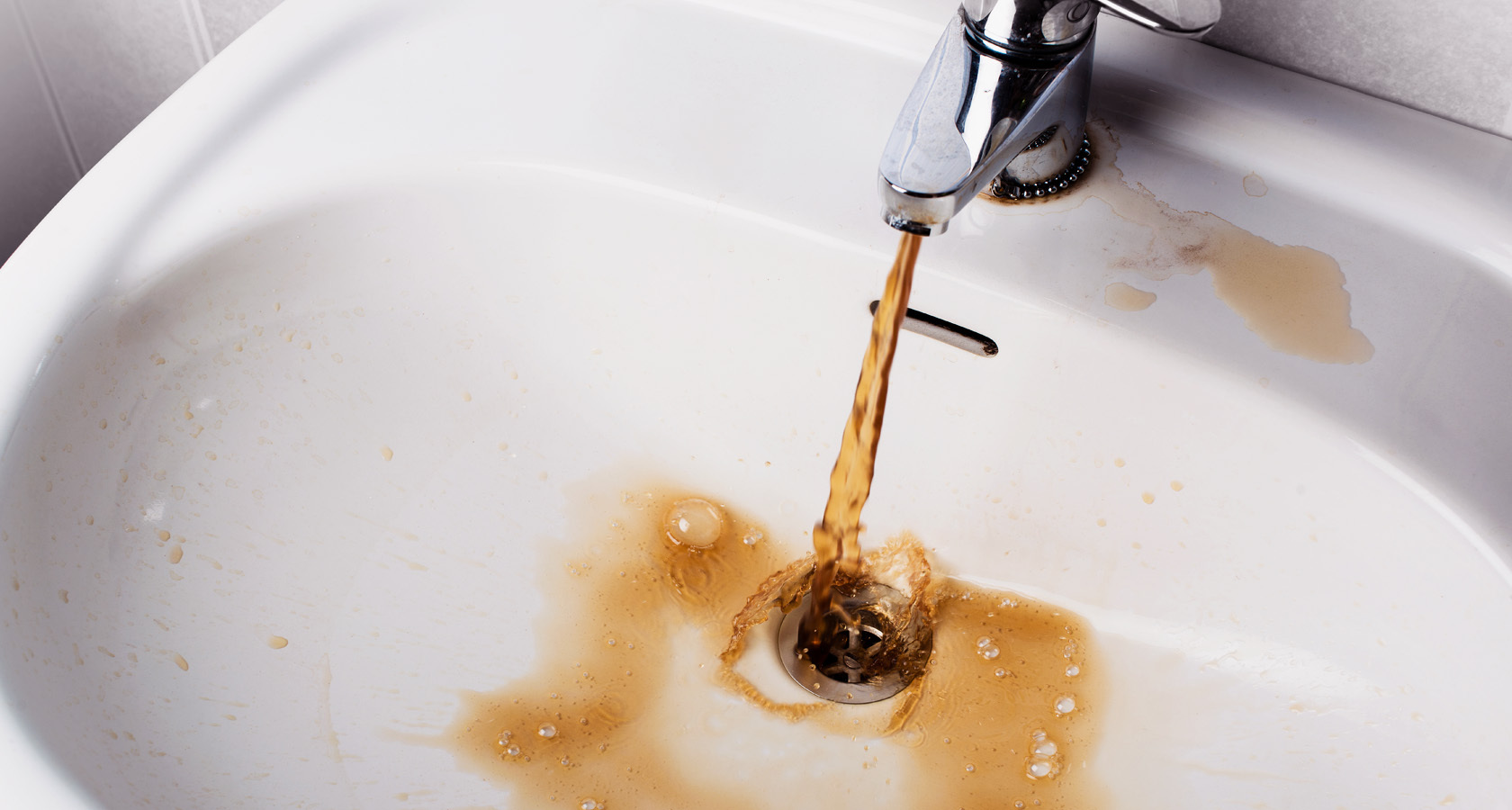
- at a low flow rate, the reservoir is filled with incoming water for a certain time, and after reaching a certain level, the pumps are turned off by a signal from a special sensor. Further, as consumers consume the water level due to the hydrostatic pressure, and, upon reaching a certain value, the sensor is triggered, the pumps are turned on, and the cycle repeats.
In the event of a pump failure or a sudden power outage, the remaining water in the tank continues to flow uninterruptedly to the points of consumption in a volume that depends on the size of the storage tank and its minimum filling level.
Scope of application
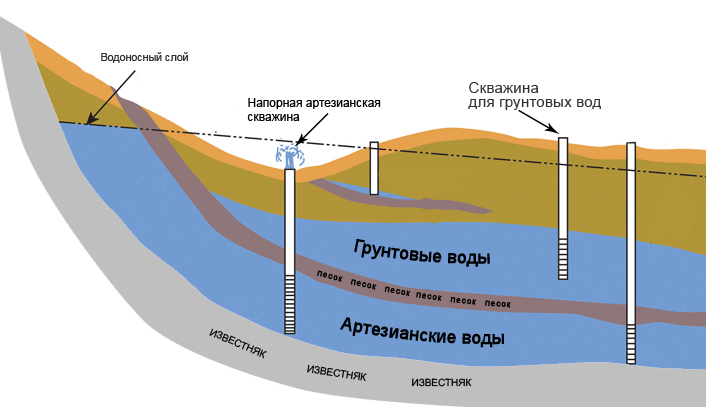
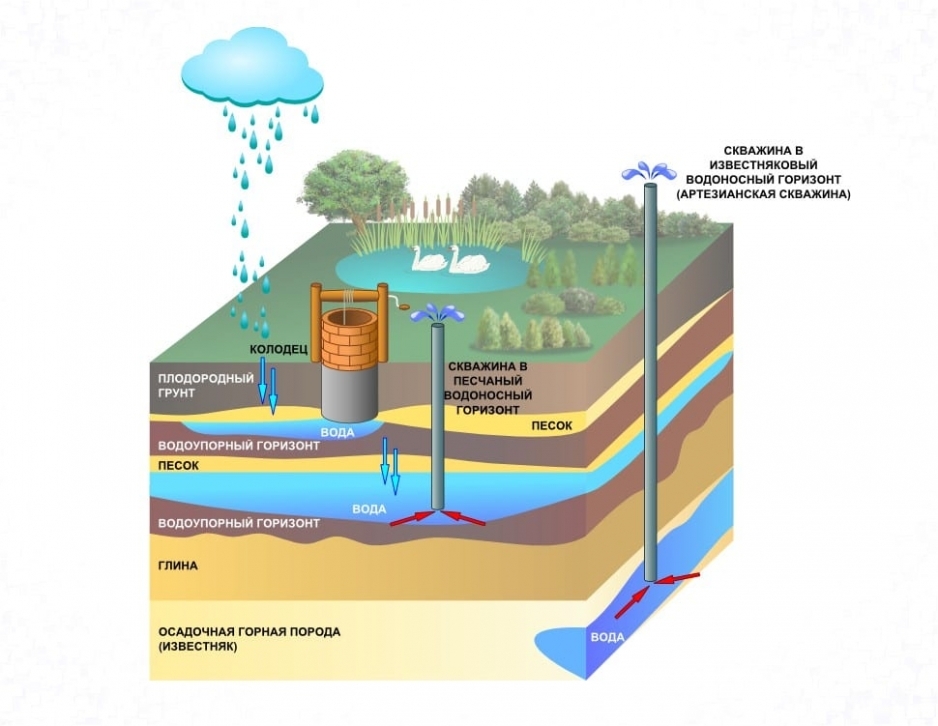
Hydraulic towers are usually installed in local water supply systems, most often in small towns and agricultural facilities. These structures are economical, they are specially designed to work in conditions of limited energy resources and are irreplaceable in their field of application.
The water tower, the creation of which went down in history as a fairly vivid example of elegant in its simplicity engineering solutions, today remains quite relevant, moreover, a necessary element of the water supply infrastructure.