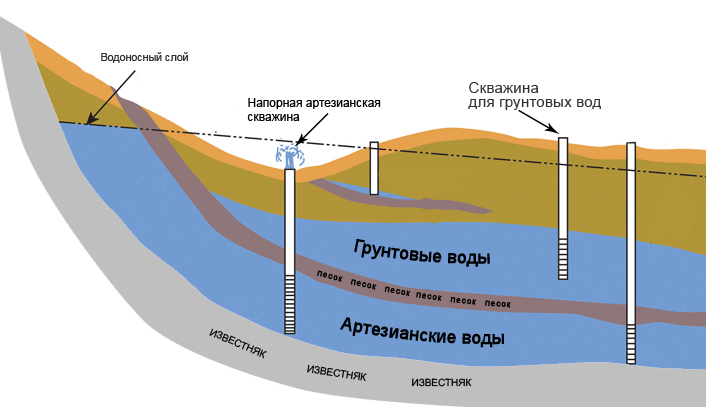
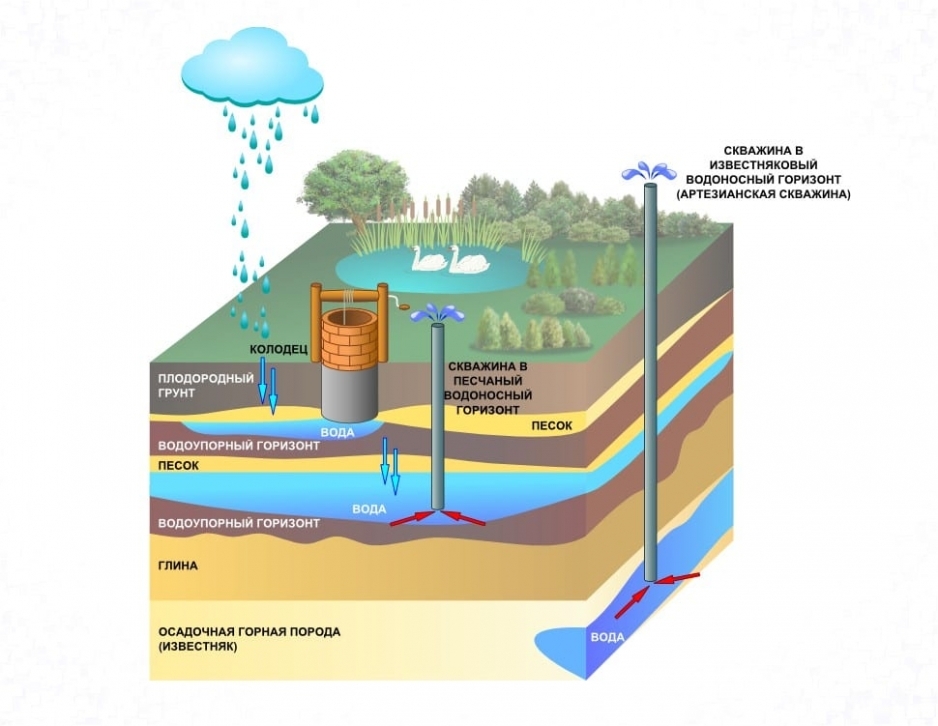
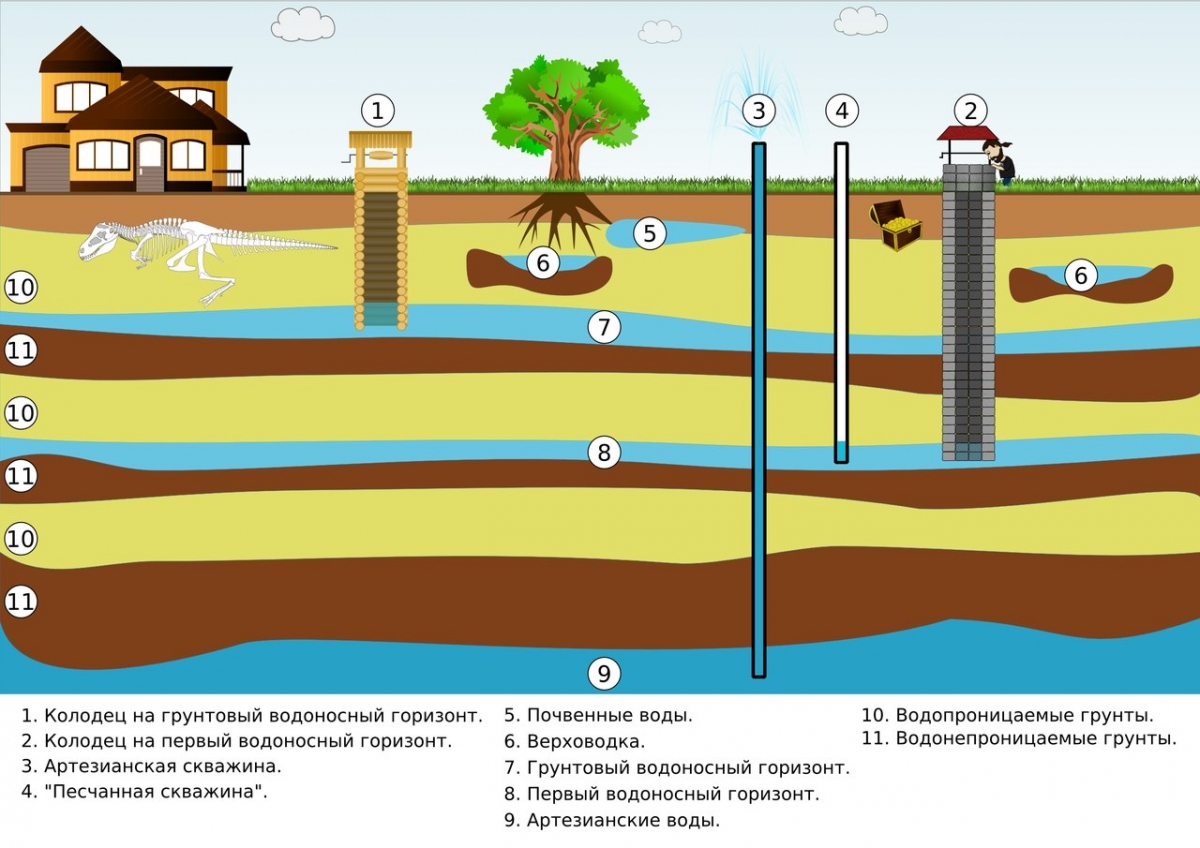
The presence of suburban areas requires the organization of an autonomous source of water supply. More often it is a well. From it, the resource goes to both household and economic needs. The owners of the plots water the garden with cold water from a well or irrigate lawns and gardens with it. This effect on crops is not always beneficial.
Is it possible to water the garden and lawn with water from a well

The flora is very demanding on the observance of biorhythms, temperature regimes, and the chemical balance of the neighboring environment. Unfortunately, only a small percentage of gardeners think that the liquid from the well is fundamentally different from the water supplied to the Vodokanal network. Resources differ dramatically in the following parameters:
- pH level;
- temperature;
- rigidity;
- third-party impurities;
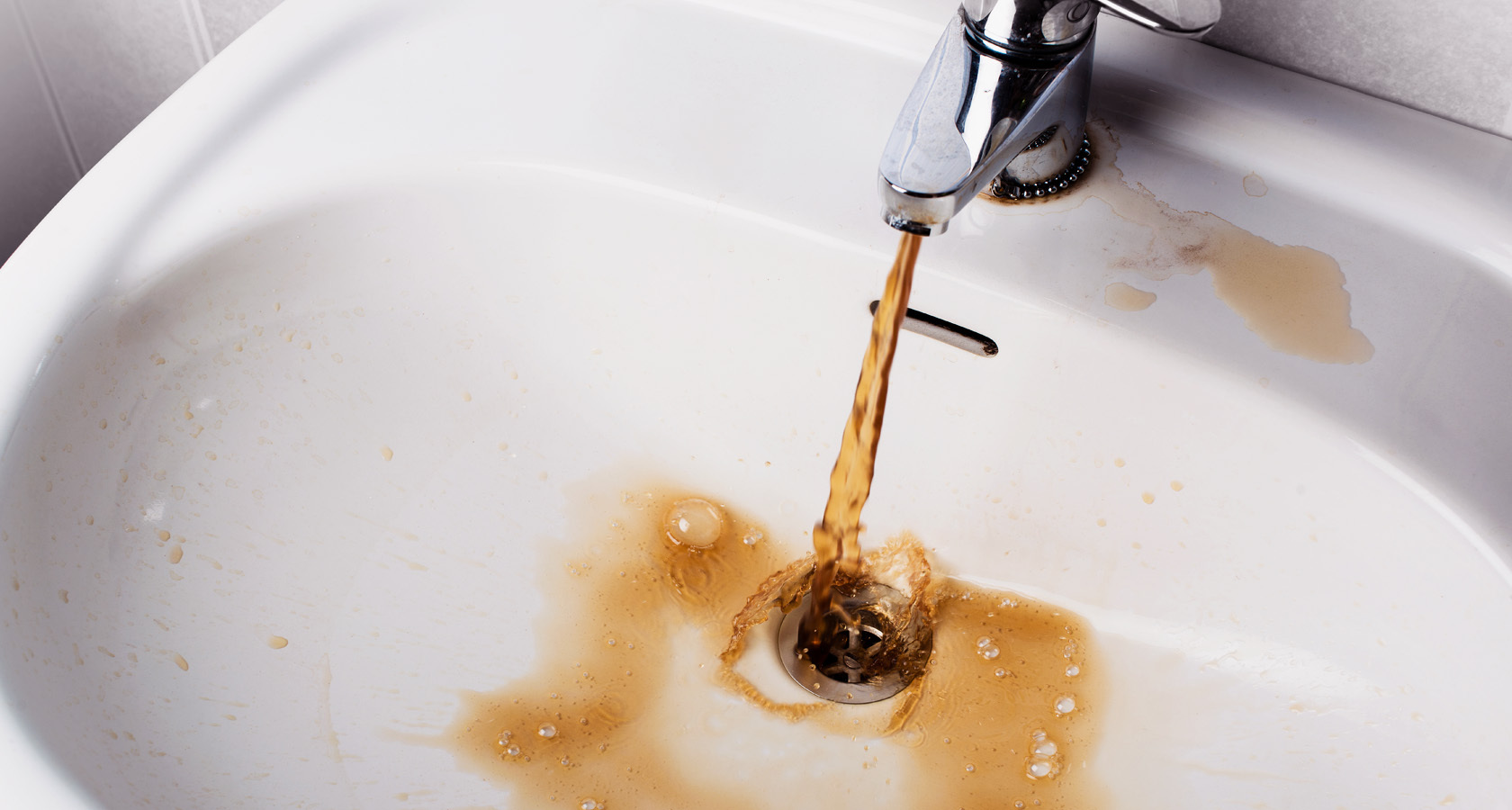
- the presence of minerals - as a rule, the water from the well is oversaturated with iron, magnesium, calcium, lime, the presence of the latter is indicated by a characteristic white coating on the leaves and soil.
Before using the liquid for irrigation from a well, it is advisable to first analyze it.
Possible dangers
When irrigating garden crops with water from a well, plants are threatened with various dangers. The most common of these are temperature shock and oversaturation with minerals, resulting in crop failure.
Temperature regime
As a rule, liquid from a natural source is supplied with an indicator of +8 - +14 degrees (in summer). The owner of the plot irrigates crops in the warm season, when the soil is warmed up to at least +22 degrees. More often than not, there is incredible heat on the street, the earth is red-hot. Under such conditions, ice water falling on the root system of the culture causes its temporary paralysis. The supply of moisture and nutrients to the aerial part of the plant for some time is interrupted. At the same time, the leaves of the culture continue to grow and evaporate. Such processes often result in the rupture of thin streams of water in the capillaries of plants. As a result, everything above this zone perishes. The phenomenon is called among professionals an apoplectic stroke. The most delicate in terms of water temperature indicators are the following crops:
- Strawberry;
- strawberries;
- bush of raspberries and currants;
- tomato;
- zucchini;
- cucumber;
- greens;
- potatoes.
The discrepancy between the temperature of the soil and the moisture supplied for irrigation should not exceed 5 degrees. Professionals recommend moisturizing the soil and plants in the evening or at night, or in the early morning hours. At this time, the sun does not burn the foliage of plants through small lens drops that form after abundant irrigation of the site.
Mineralization
If the analysis showed an excessive saturation of the liquid with minerals, it is better to immediately install a good water purification system, because the site owner also uses it for domestic purposes.
Calcium and iron especially negatively affect such crops:
- coniferous trees;
- Apple tree;
- viburnum and mountain ash;
- hydrangea;
- lily of the valley;
- maples and other lovers of acidic soils.
In addition to the fact that the admixture of iron has a negative effect on the soil and crops, it also very quickly destroys all the nozzles and other metal elements of the irrigation system. The same effect is observed from resources oversaturated with chloride salts or limestone. Salt water should not be watered at all. All living things will gradually perish.
Manganese burns the soil seriously. Later, it becomes unsuitable for planting and growing plants.
Oxygen saturation of water
The moisture supplied from the well is practically not enriched with oxygen. It is undesirable to irrigate garden and garden plants with such a liquid. The exception is when water is supplied through drip irrigation systems or sprinklers. If watering is carried out through a hose directly from the source, one can not talk about the saturation of the O2 resource.
To saturate the water taken from the well with oxygen, you need to make special sedimentation tanks for it: large barrels, vats, a pool. First, they are filled to the top and the liquid is allowed to be saturated with life-giving gas.
Do I need to heat the water from the well before watering

Experts assure that heating is the only way to protect a garden, lawn, or vegetable garden from death. Special storage tanks are filled with borehole water. In them, the liquid should settle for about a day or more. During this period of time, the following will happen:
- The water will warm up to the optimum temperature. As a result - the exclusion of shock in plants when they are irrigated.
- It will be saturated with oxygen, it will become alive, suitable for moisturizing the soil, the root system of crops.
- It will settle, as a result of which all iron ions oxidized by oxygen will precipitate. This does not require an expensive cleaning system.
- Carbonate salts will linger on the walls of the storage tank.
- The density of the water will change in height. Its upper layers will be less mineralized. Use moisture from this part of the drive.
Thus, a natural purification of the liquid is obtained. It is desirable to have such a volume of storage tanks so that new liquid can be gradually added to them, taking some part earlier.
It is allowed to ignore the temperature regime if water is supplied using aerators. Liquid droplets are heated in the air before falling to the ground.
In order to qualitatively moisten the soil in the garden, vegetable garden, on the lawn during the hot period, 500-1000 liters of water should be consumed per one hundred square meters of the plot.