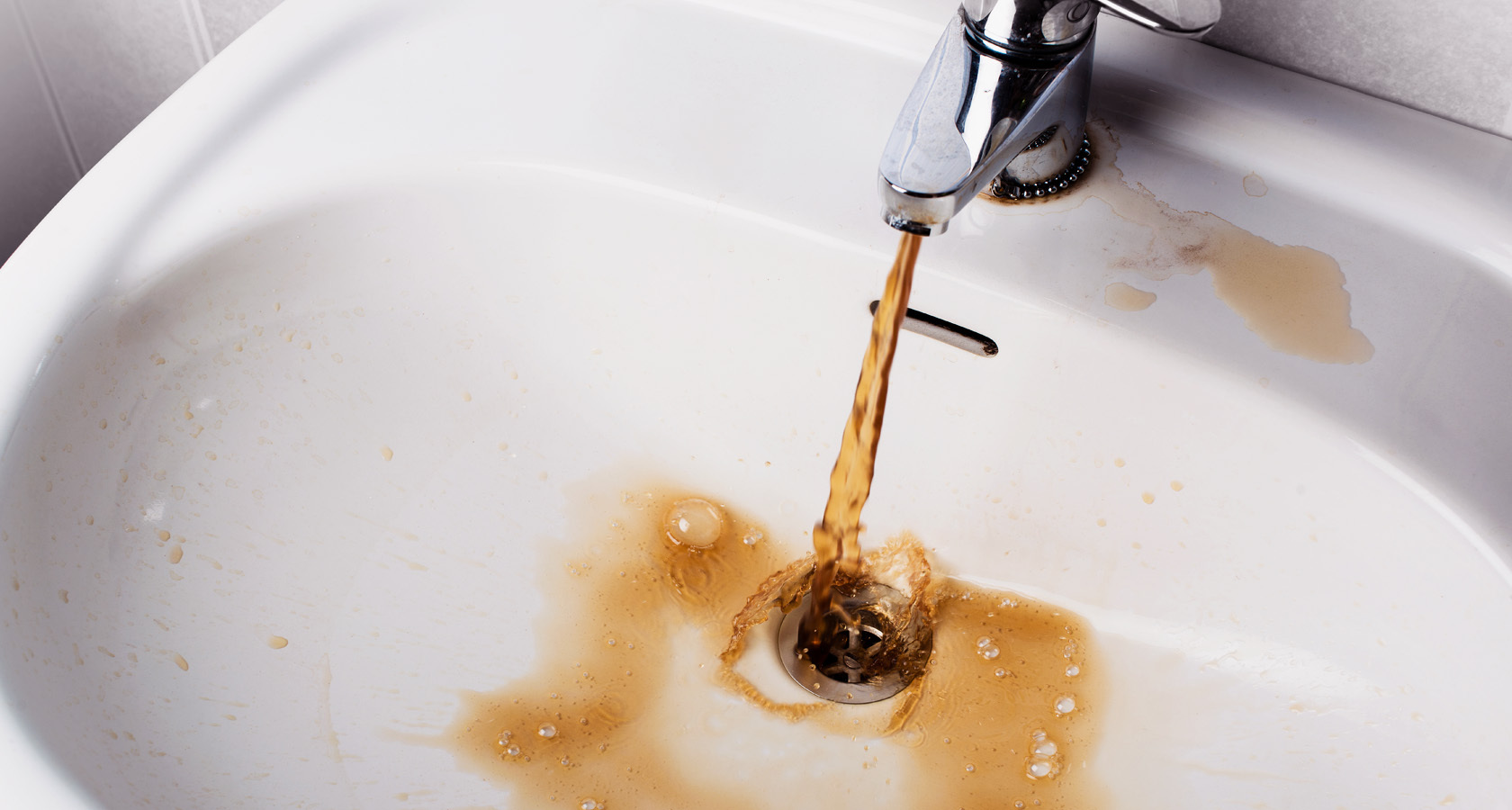
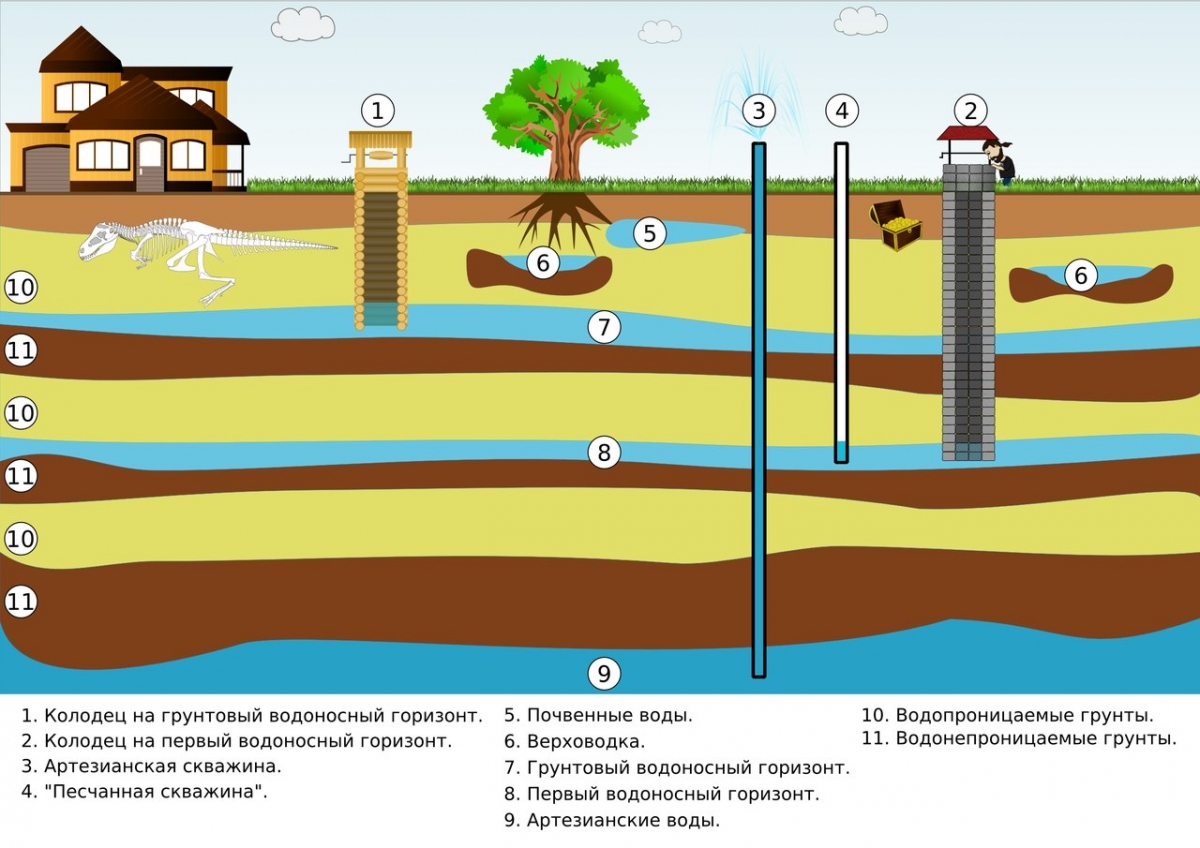
Decentralized water supply involves taking water from underground sources for drinking and household needs without delivering it to its destination. Most users have developed a strong belief in the safety of underground storage facilities for moisture that has passed through the filtering layers of the soil. But this misconception is refuted by the indicators of liquid samples taken in various areas.
Definition of decentralized water supply and its differences from centralized
In cities and towns covered by main water pipelines, water is supplied from the source to the place of use through a pipeline system. A complex scheme includes:
- underground storages or open reservoirs where water is taken;
- water treatment complexes, consisting of facilities for filtration and obtaining liquid with the required quality level;
- reservoirs for clean water;
- distribution stations;
- backbone networks;
- water pipes.
The list of elements indicates a fundamental difference between the ways in which the population is supplied with water. Water supply in rural areas does not have water treatment complexes, distribution stations and main networks. The role of clean water reservoirs is taken over by domestic vessels, into which the brought water is poured.
Actual requirements
The state attaches great importance to the protection of natural sources. On November 25, 2002, Resolution No. 40 was issued on the approval of SanPiN, which impose certain requirements on the composition and quality of water extracted from wells and wells: smell, turbidity, hardness, content of mineral compounds and taste. For field water supply, criteria are approved that must be followed when choosing places for water intake, as well as the rules for their arrangement.
Survey of an underground source includes data on water quality and sanitary condition of the surrounding area. Information is collected on possible causes that can cause contamination by microbes or toxic substances.
Choosing a location for the source
Relevant data on the places of water intake are contained on hydrogeological maps, which are compiled on the basis of sanitary and geological exploration studies carried out in a given area.
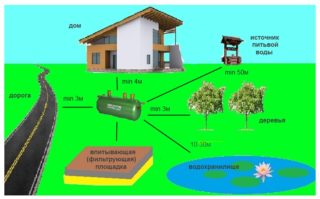
The presence of burials and cattle burial grounds, storage sites for pesticides, landfills, cesspools and other objects polluting nature is not allowed near the selected point. To prevent groundwater from getting into a well or a well, they are settled at least 50 m higher up the slope from the channel of the rain flow.
It is unacceptable to organize a water intake point in swampy or periodically flooded areas, as well as in places where landslides are possible. It is allowed to locate an artificial source at least 30 m from busy highways.
Construction and equipment of water intake facilities
- mine wells;
- artesian wells;
- springs.
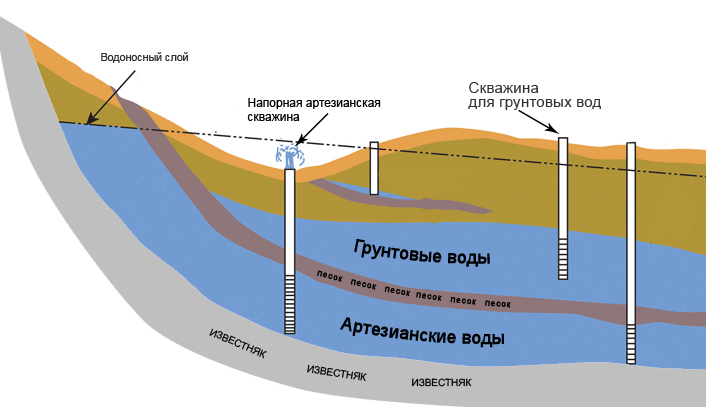
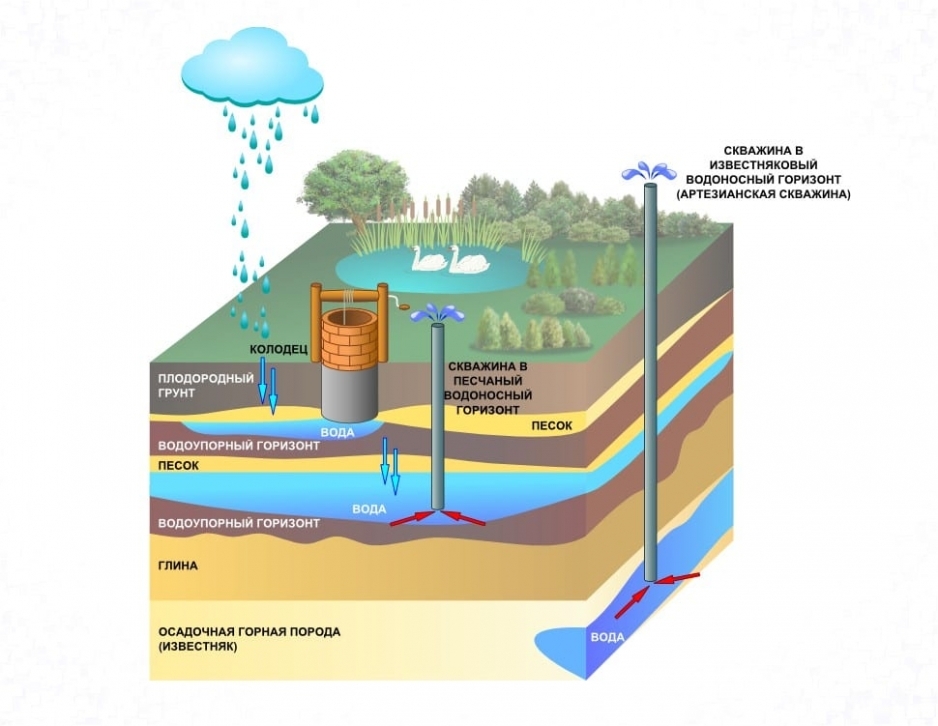
Aquifers can be located at different depths. If they are close to the surface, they dig a well, which collects liquid that has passed through a natural filter from sedimentary rocks. The shaft can be round or square.
The device includes:
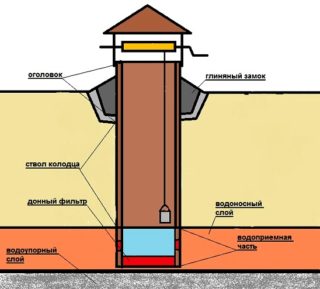
- the upper element of the barrel structure, called the head (superstructure over the source);
- shaft, lateral surface of the mine;
- the cavity in which moisture is collected, i.e. water intake.
The head protects against dirt and falling of animals and people, therefore, the height of the structure above the surface should be 0.8 m. The well is closed with a lid or a canopy is erected above it. Sometimes a special structure is adapted for this.
The “castle” made of compacted clay, the depth / width of which is 2/1, as well as a blind area along the perimeter of two meters around the device, made with a slope from it, are designed to protect the well from landslides and destruction, runoff or seepage of surface water. For safety, the wells are fenced, a pedestal for buckets is arranged nearby.
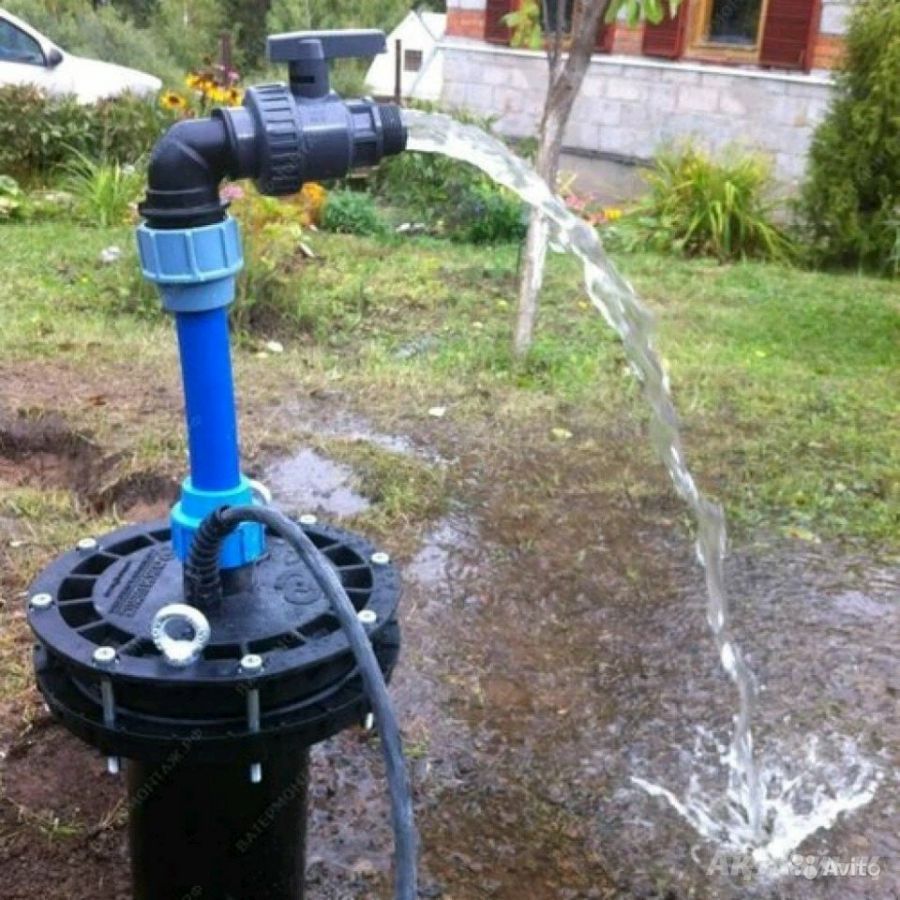
Wells are tubular wells that can have a depth of more than 100 m. They are equipped with casing pipes. To raise the water, a pump with a filter to prevent clogging is used. The superstructure on the surface is carried out similarly to conventional wells, with a blind area and a bench. The head rises to a height of 1 m, the well is closed with a casing, water is supplied through a drain pipe, on which a bucket hook is welded.
Capturing wells are arranged for the intake of spring water. They are of two types:
- descending - water flows from the wall of the well;
- ascending - there is a cavity for collecting liquid.
They also have a fence, are equipped with a water intake, an overflow system and a hatch. Water intake is carried out from a pipe with a diameter of at least 10 cm. Captages are placed in pavilions and supplied with a pipe for removing stagnant odors.
Maintenance and operation of water intake facilities
Respect for the source implies compliance with the rules for its operation:
- it is unacceptable to wash machines and wash clothes at a distance closer than 20 m from the capturing;
- if the well is not equipped with a pump, water is collected in a public bucket, from where it is poured into the brought containers; you cannot use household utensils for this purpose and scoop out water from a public bucket with the help of a ladle brought in.
In winter, the well needs to be insulated with the help of environmentally friendly materials, which are allowed by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for household and drinking sources. Sawdust and shavings from woodworking shops are suitable for this purpose. In cold weather, the sediments need heating.
Once a year or as needed, the wells are cleaned, scooping up the remaining liquid, and repairs are carried out, along the way, carrying out disinfection measures. If a decision is made to dismantle the well, they fill up the well, tamping the soil tightly.
Water quality control
To ensure safe water use, sanitary and epidemiological surveys of wells and the surrounding area are periodically carried out. This rule applies to functioning and new commissioned structures.
If the sanitary indicators deviate from the norm, re-sampling is done for control. If deterioration is proven, action is taken to identify and eliminate the cause of the infection. This work is carried out by specialists who clean and disinfect the well. If it is not possible to eliminate the source of chemical poisoning, the water intake device is eliminated.