Bringing the indicators of tap water (borehole, well) to the optimum in terms of the amount of salt content is one of the main tasks of preparing a drinking resource. Otherwise, the liquid is not ready for use and causes irreparable harm to health, any technique. For high-quality processing of the source material, special installations for water desalination are used. They differ in the way they act on the liquid.
Purpose and scope of the desalting method

Desalination is the process of qualitatively reducing the concentration of mineral impurities in a liquid medium to the values recommended by GOST and SanPiN. This indicator should not exceed 5 mg / l. Do not confuse the method of liquid processing with desalination (seawater preparation).
Desalting is a reliable treatment method for further use of the liquid in the following industries:
- pharmaceutical industry;
- microelectronics;
- branches of medicine;
- chemical industry;
- heat power engineering;
- household facilities, etc.
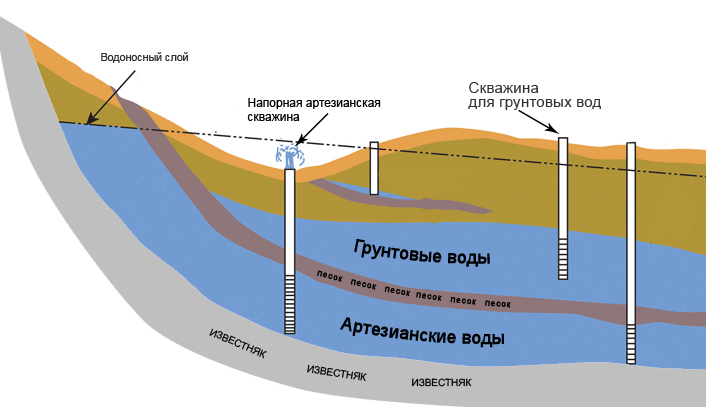
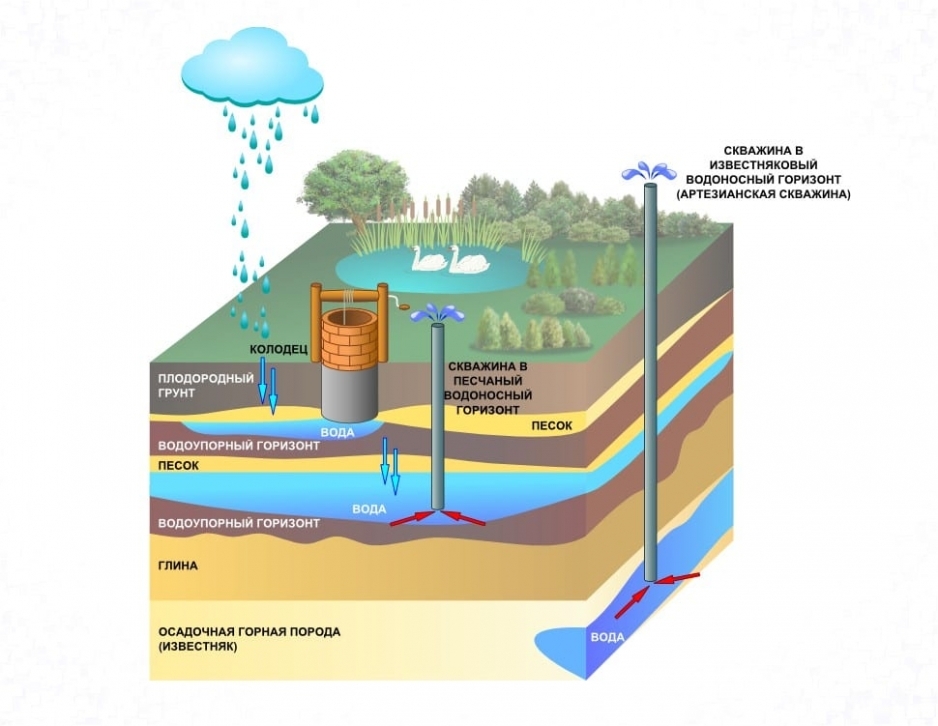
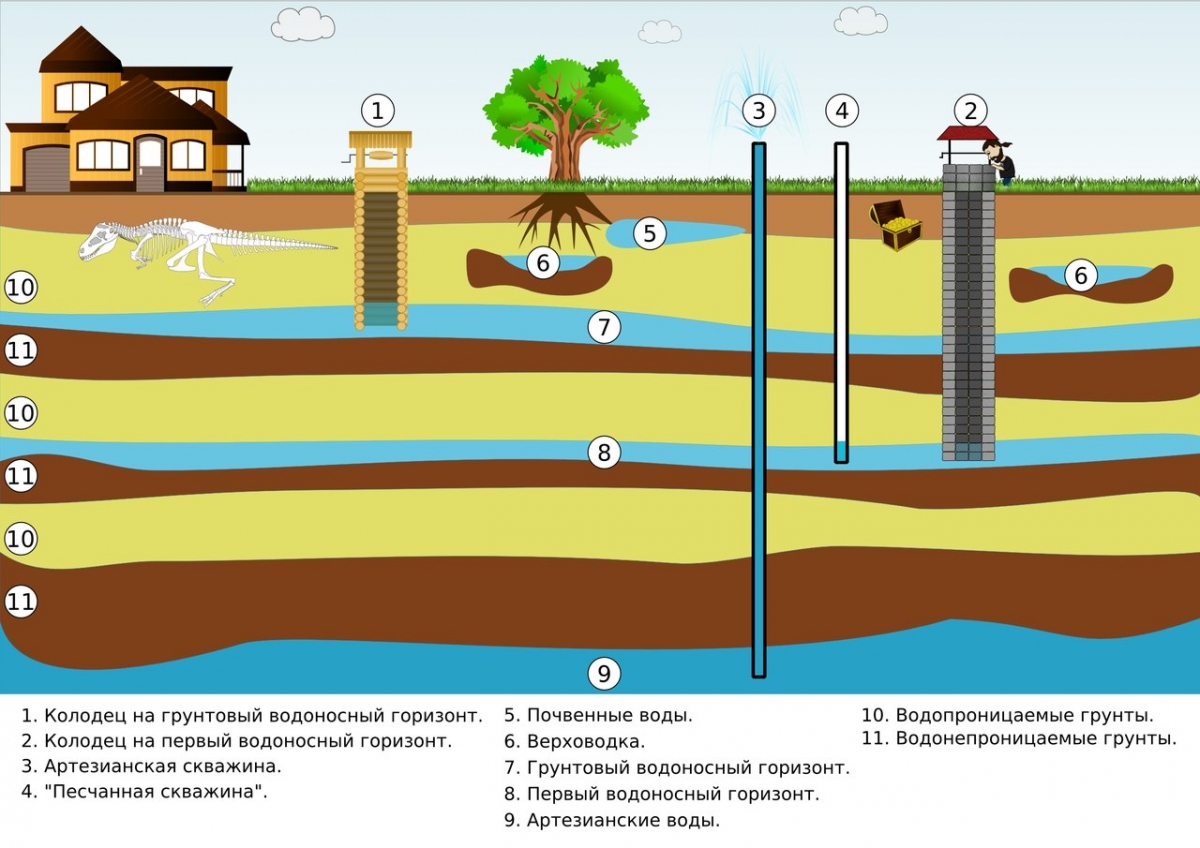
Liquid medium treatment methods imply a change in the aggregate composition of water or its absence. A change in the state of aggregation is a method of boiling, freezing for an hour or more, and distillation. They are more often used in everyday life. In the second case, electrodialysis, ion exchange, and reverse osmosis are used.
Water demineralization methods
Ion exchange
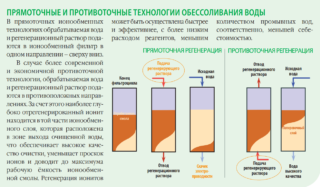
The principle of processing a liquid medium is to run it through special ion-exchange resins. In this case, anions and cations of mineral impurities dissolved in the liquid are removed and replaced by ions of the filtering material. With this method of desalination, it is possible to almost completely remove mineral dissolved impurities from the liquid medium.
The ion exchange unit is a tank filled with filter cartridges. The cassettes must be replaced regularly and the resin itself must be disposed of in a special manner.
Reverse osmosis
Electrochemical method
The essence of electrodialysis is that an aqueous medium is exposed to an electric field - it is passed through it. At this moment, the transfer of ions of dissolved salts occurs: anions are distributed to the anodes, cations - to the cathodes.
The device for electrodialysis has three chambers formed by the anode and cathode diaphragms. The middle compartment is a reservoir through which the processed liquid passes. A current is passed through it, which then divides the salt ions into cathodes and anodes.
Pros and cons of methods
Ion exchange units are distinguished by the following advantages:
- obtaining the most pure water;
- high reliability;
- lack of response to the degree of mineralization of the treated medium;
- low equipment costs.
The disadvantages of the ion exchange method include:
- the complexity of the disposal of waste filter material;
- environmental pollution;
- the need for regular filter replacement.
The maintenance costs of the ion exchange system vary in proportion to the concentration of salts in the liquid.
For a reverse osmosis installation, the following advantages are characteristic:
- inertness to the initial composition of the liquid;
- ease of installation maintenance;
- no need to use complex reagents;
- the ability to dump waste concentrates into the sewer;
- high quality neutralization of mineral impurities;
- low system maintenance costs.
The disadvantages of reverse osmosis are:
- the need for pretreatment of the liquid;
- high volume of discharges;
- the need for continuous operation of the installation;
- relatively high energy consumption for industrial scale cleaning.
Reverse osmosis units are installed in private houses and apartments under the kitchen sink.
Electrolysis is not used in everyday life, since the cost of electricity and the installation itself is impractical.
More often at home, they use a thermal method of processing (boiling) or filtration through carbon cartridges. However, this only softens the liquid, but does not get rid of mineral dissolved impurities.