As the main purpose of the check valve on the water supply system, the craftsmen highlight the organization of the direction of flow in one direction. In addition, with the help of reliable fittings, it is possible to prevent leaks in the system, a decrease in pressure in the pipeline or accidental shutdown of pumping equipment (for autonomous communication).
Definition and purpose

A check valve is a type of shut-off valve for a water supply system. Thanks to such a device, the master organizes the direction of the flow of the transported water and excludes its reverse flow. Application area:
- cold and hot water risers in apartment buildings;
- individual water supply systems in a residential area (including autonomous private communications);
- vibrating submersible pumps;
- autonomous water stations equipped with a pump;
- cold water supply inlet at storage boilers;
- installation of boiler equipment, etc.
The shut-off valves are installed in accordance with the arrow-pointer on it.
Principle of operation
The non-return valve works thanks to the built-in shut-off mechanism. It is made either in the form of a ball or in the form of a petal. The principle of operation of the fittings is as follows:
- The water moves in a given direction, increasing the inlet pressure to the valve.
- The locking mechanism opens and allows water to flow forward.
- As soon as the movement of liquid through the pipeline stops, the pressure in the network drops - it is equalized at the inlet and outlet to the valve. The locking mechanism closes, thereby preventing reverse current flow.
Additionally, the volume of water in the system supports the locking ball / petal, preventing it from opening.
Types and device
The classification of shut-off water valves occurs according to several parameters. At the place of installation of the check valve in the water supply system:
- Pipeline. Designed to prevent pressure drop in the system. If a check valve is not installed on the water supply, water will flow down again when the tap is closed. Serious losses are generated in the network. The water meter counts only the forward flow of the liquid.
- Bottom. They are installed on a section of a vertical pipeline leading from a well / well to a pump.
Depending on the design of the internal locking mechanism, the following types of check valves are distinguished:
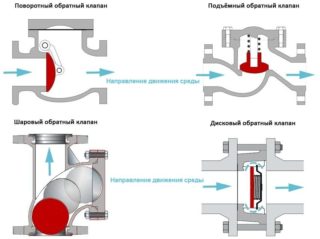
- Ball. It has a locking ball in its design, which is pressed against the device seat by a special return spring. Most often, such a check valve is used on household water supply and small-diameter pipes.
- Lifting. Equipped with disc locking mechanism. Moves up / down depending on the pressure change in the system. When changing the direction of fluid flow, the valve closes the valve lumen. The lifting mechanism may only be installed on a horizontal pipeline with clean water.
- Turning. It has a shut-off mechanism in the form of a flap, which swings back when the pressure in the network changes. The return spring helps the sash to close when the water flow stops and does not let it back. The swing check valve can be installed on large diameter pipes and on water with impurities.
In order to avoid possible water hammer in a system with a lifting mechanism, it is important to strictly observe the “top” marking on the valve.It is also advisable to observe the maximum slope and additionally use water hammer damping elements.
According to the installation method, water return valves are:
- Flanged. They are mounted on cast iron pipelines. Fastened with flanges.
- Interflanged. In addition to flanges, special metal studs are used for fastening.
- Coupling. They are mounted on a threaded connection. They are more often used in household piping.
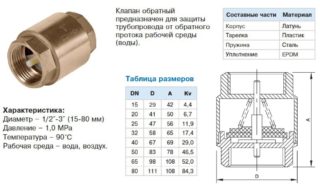
According to the material of manufacture, check valves are cast iron (the most inexpensive ones used on city highways); brass (reliable, corrosion-resistant, household); stainless steel (the most expensive and high quality).
Check valve dimensions
- 1/2 "- Has a very low flow rate. It is rarely used.
- 1 inch is the most common device for a household water supply system.
- 1 ¼ - designed for large highways.
- 2 inches - placed on wells and in autonomous, suburban water supply systems.
- 3/4 - designed for central highways.
The valve must be of the same diameter as the pipeline on which it will be installed.
The nominal size of the reinforcement can be from 10 to 400 mm.
How to choose fittings
When choosing a check valve, an experienced craftsman pays attention to the following parameters:
- The size. If you buy smaller valves and still install them using adapters, the reliability of the mechanism will be in doubt. In addition, the resistance to the moving stream will be increased.
- Appointment. For example, lift check valves must be mounted in a strictly specified position, forming a stroke perpendicular to the ground.
- Material. It is better to use a steel or brass mechanism on hot water pipelines. Polymers quickly break down when exposed to high temperatures.
- Docking method. For domestic water supply, coupling valves are often used to avoid additional adapters on the pipeline.
It is better to purchase shut-off valves in a specialized store. There, the buyer is given a check for the goods. On the basis of this, you can exchange the product or return it.
Installation features
Choosing the right check valve is only half the battle. Next, you need to correctly mount it. Otherwise, the device will fail many times faster. This will entail additional hassle and financial costs. When installing a check valve, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Arrow on the case. Its direction should point towards the water flow in the system, both with horizontal and vertical installation of the fittings at the inlet.
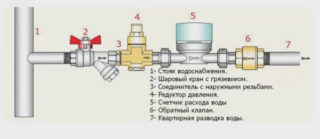
- You need to put the part right after the water meter, where the branching of water begins to different plumbing points. Thus, the meter will accurately determine the amount of water consumed per apartment / house.
- Coupling devices are installed by cutting the pipe in the desired area behind the water meter. A thread is cut into the ends of the tube. Then put on the check valve and tighten it with nuts at both ends.
A properly installed mechanism should not allow water to flow back. If this is the case, the valve is defective or the installation has gone wrong.