Compliance with the regulations for the use of water protection zones is part of a set of measures to protect nature, improve the sanitary and ecological state of water use facilities and improve the near-water area. The rules for the operation and maintenance of the water supply system are described in a specialized section of SanPiN, which also establishes sanitary and hygienic standards for environmental objects.
Water supply security zone
The rules for using the water supply are spelled out in SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02, which has legal force and is a document of title for the use of individuals and legal entities.
With regard to the use of water supply, environmental measures are aimed at reducing and reducing pollution. The regulation is aimed at different types of objects:
- superficial;
- underground;
- artificial.
When studying, accounting and applying the rules of water use, it is necessary to take into account that the objects are classified and distributed by zones.
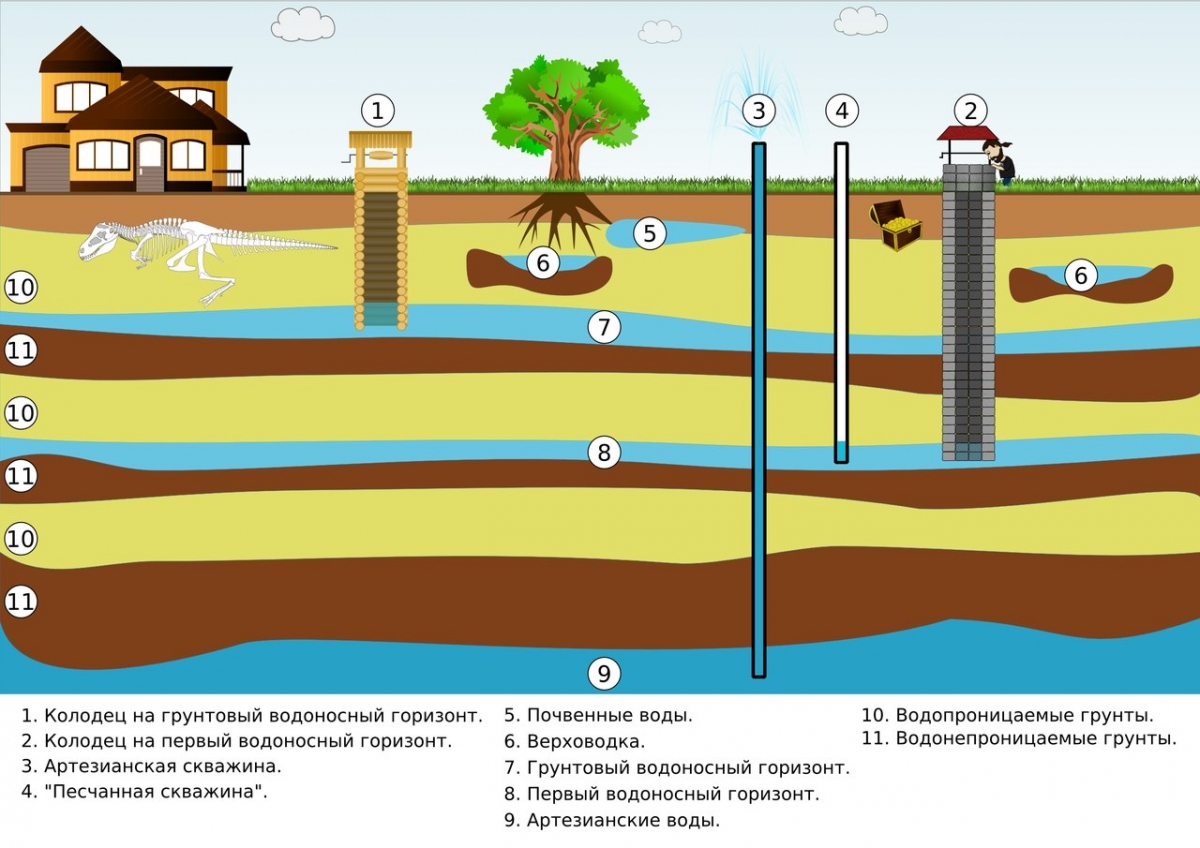
Surface Objects
- The first belt is the intake structure. It is considered a security facility with a pass system with a guarded adjacent territory, the size of which is determined in accordance with the dimensions of the buildings.
- The second belt imposes restrictions on the territory adjacent to the first; any buildings are prohibited here. The boundary of the belt is determined individually, depending on the size of the territory and the source, the speed of water movement, which are necessary for the self-purification of the water body.
- The third belt performs an observation function. There are no restrictions on use, monitoring is underway.
Information signs are placed on the boundaries of the security zones, and a fence is placed on the boundary zones of the security zones.
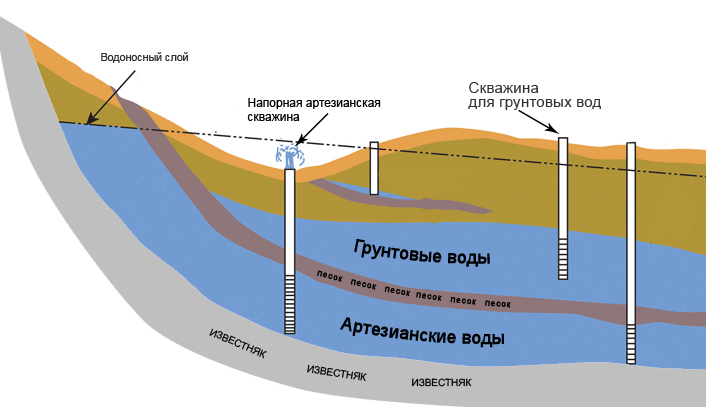
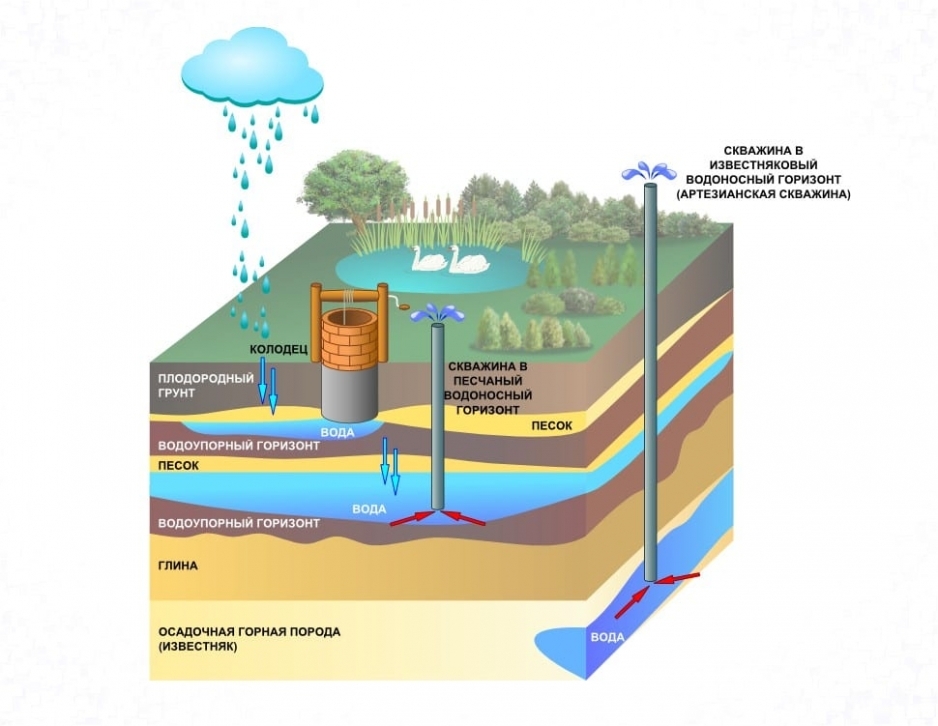
Underground facilities
- First belt. The security zone of the water supply system according to SNIP is from 25 to 50 meters. Any buildings, except for those related to the water intake, are prohibited. These include pumping stations, water towers and outbuildings. Access is granted to employees, technicians, and engineering teams troubleshooting the system. The area is separated by a fence.
- Second belt. It is calculated using hydrodynamic laws and climatic-dendrological conditions, determining the area of possible contamination of the adjacent territory for a period from one hundred to four hundred days.
- Third belt. Located in the area where people live. The estimated operating time of the water well is 25 to 50 years. Based on the calculations, it is generally accepted that pollution from human activities will reach water intake much later than this period.
The sanitary protection zones of the water supply system are marked on the maps and delimited by special signs.
Artificial objects
Water intake from structures outside the water intake is considered to be an artificial object of water use. Zones of sanitary and hygienic protection that are not on the territory of water intake from natural sources arrange around:
- filtration stations and storage tanks - up to 30 meters;
- pumping stations, warehouses with chemicals for water supply and sedimentation tanks - up to 15 meters;
- water towers - up to 10 meters.
Sanitary restriction strips with a width of ten to fifty meters are laid near the water conduit, depending on the level of groundwater and the diameter of the water pipes.
If water canals are laid across populated areas, it is allowed to reduce the protected zones based on the results of agreement with the SES.
The area of protected areas of water pipelines is regulated by SanPin 2.1.4.1110-02. The following dimensions are set for the minimum boundaries:
- at least five meters from the foundations of buildings and structures;
- at least three meters from supports, fences and highways;
- at least two meters from road markings;
- at least one meter from power transmission towers.
There should be no latrine pits, garbage facilities, manure storages, garbage collectors and other structures that could pollute aquifers in the protection zones of water pipelines. It is forbidden to build water conduits in landfills, sewage and filtration fields, industrial enterprises, churchyards and cattle burial sites.
Responsibility for violation of security zones
- Compensation for material damage caused as a result of unauthorized construction, illegal storage and accumulation of garbage in the protected area.
- Fines for violations of the rules of regulatory documents during construction.
- A criminal penalty is imposed for the seizure of protected areas.
If a violation is detected, ignorance of the boundaries of the water protection territory is not an excuse. Before starting construction or carrying out land works, permits should be agreed with the water utility department.
If there are no information signs or other restrictive measures, the operating organization is responsible for the safety of the territory. If all informational and protective elements are present in the zones of sanitary and epidemiological restrictions, the offender bears responsibility.
In accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses, a fine is imposed for violation of the regime in protected areas:
- civilians from 500 to 1 thousand rubles;
- officials from 1 to 2 thousand rubles;
- legal entities from 10 to 20 thousand rubles.
Fines are determined in accordance with the version of the Federal Law of June 22, 2006 No. 116 - FZ.
Failure to comply with the requirements for bringing environmental zones near water pipelines to a state suitable for use entails liability:
- for individuals 3000 - 5000 rubles;
- for officials 3000 - 5000 rubles;
- for legal entities 20,000 - 30,000 rubles.
As amended by Federal Law No. 282 dated October 21, 2013.
Failure to comply with the requirements for the protection of water bodies, entailing their pollution or depletion, threatens with a fine:
- for individuals 1500 - 2000 rubles;
- for officials 3000 - 4000 rubles;
- for legal entities 30,000 - 40,000 rubles.
Since ignorance of the law does not exempt from liability, before starting any work, it is necessary to agree on the project documentation with the regulatory authorities in order to avoid damage to natural resources.