The rules for the technical operation of systems and structures of public water supply and sewerage are a regulatory legislative document that is the basis for the work of enterprises engaged in water supply to the population and organizations. The rules clearly indicate what water supply organizations should do, what their duties are, how work and regime are arranged, how quickly they should respond to emergency and non-standard situations.
General provisions for the operation of water supply and sewerage systems
It mentions several documents that are the main organization of work:
- SNiP II-32-74 - a set of rules for the protection of surface waters from sewage pollution;
- instructions for receiving industrial wastewater into the city sewerage system;
- GOST 2874-78, which determines the parameters of water quality.
Based on these documents, the work of the enterprise is drawn up. In order for it to be organized competently, you need:
- highly qualified specialists;
- control, accounting and analysis of working conditions;
- clear organization of rational modes of operation of both water supply and sewerage;
- automation and mechanization of production cycles;
- organization of conditions for prevention, inspection and repair of networks, equipment;
- study and registration of the causes of emergencies.
The complex of ongoing activities is focused on two main points: technical personnel and equipment. With the employees of the organization, training briefings are held all the time, in which the rules for the work of each employee individually and the team as a whole are mentioned several times.
Moreover, each employee periodically undergoes advanced training outside the walls of the organization. For this, courses, schools are organized, in which they provide information about new products that have appeared in terms of installed equipment or technologies for water supply and sanitation.
All employees and employees strictly adhere to the above stated rules. Anyone who does not fulfill the conditions is subject to strict administrative measures. There are frequent cases when violators were criminally liable.
Dispatching service

The assignment of the dispatch service clearly describes what dispatchers should do, what powers they are endowed with.
- Manage networks by maintaining specified modes.
- They control the conduct of emergency, repair and preventive work.
- They accept applications from the public or organizations.
- Provide the maximum amount of water for large fires.
The structure of the dispatching service depends on the complexity of the water supply and sewerage networks, on their productivity, length and complexity of technological processes. The dispatching service is subordinate to the chief engineer of the enterprise, but in operational terms it is subordinate to the dispatching service of the higher organization.
The dispatcher on duty provides technical guidance for the water supply and sewerage system.He can make inquiries on the technical condition of the equipment, lead teams that leave on request. He is also responsible for reporting the duty shift, fills in the required journals, keeps in touch with all services of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. If necessary, his duties include providing information to local self-government authorities.
The cabinet must have:
- schedules and operating modes of water supply and sewerage;
- regulations for the maintenance of water pipelines and sewerage networks;
- instructions and rules;
- system diagrams and types of equipment;
- list of phone numbers of the management: home and mobile;
- list of telephones of city services
Dispatchers work according to the established and approved schedule. They are considered operational workers, in whose hands all the work of the water supply and sewerage systems. The powers of these employees are large - up to the disconnection of networks, if there are reasons for this. They do not need orders, all decisions are made independently on the basis of instructions and rules.
Sanitary protection zones
- In all settlements, sanitary zones must be established without fail.
- They are coordinated with the local authorities of the State Sanitary Inspection and are developed on the basis of SNiP II-31-74.
- Approved by local government authorities.
- Responsible for the supervision of the zones are appointed by order of the head of the organization dealing with water supply and sanitation.
- In the first sanitary zone, it is forbidden for people to build and live, to dump drains, grazing and watering livestock, bathing are prohibited. You cannot fish, wash clothes, etc. Such zones are guarded.
- The second zone is the territory in which construction can be carried out, but agreed with the State Sanitary Service. The main requirement is not to reduce the quality and quantity of sources that are used for water supply. The area is patrolled by guards.
If the source of water supply in the second zone is a river, control over the implementation of measures related to the prevention of pollution emanating from river transport is strengthened. This is a complex event, which is coordinated with all city services.
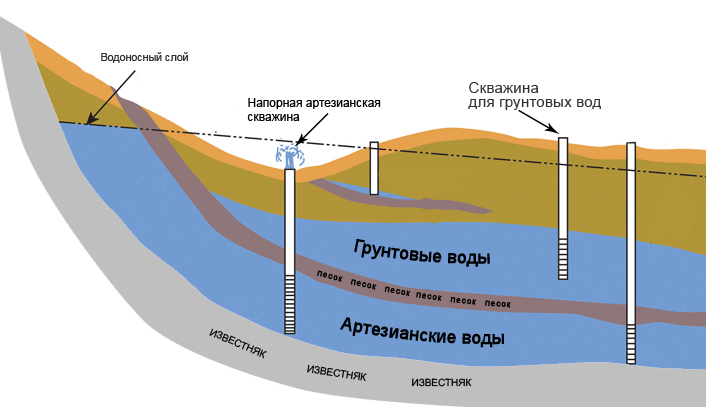
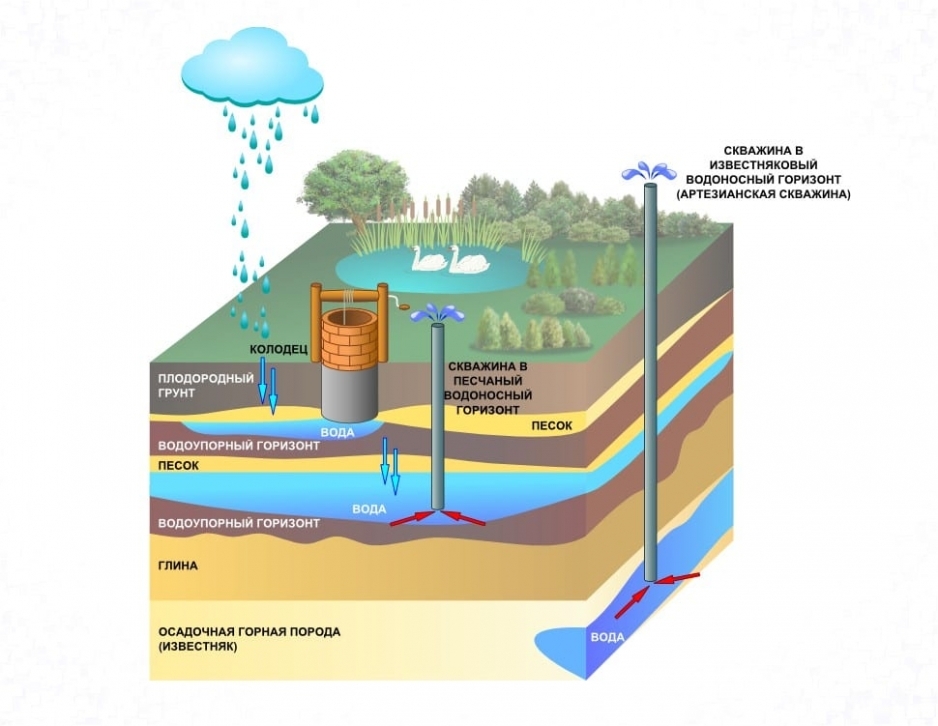
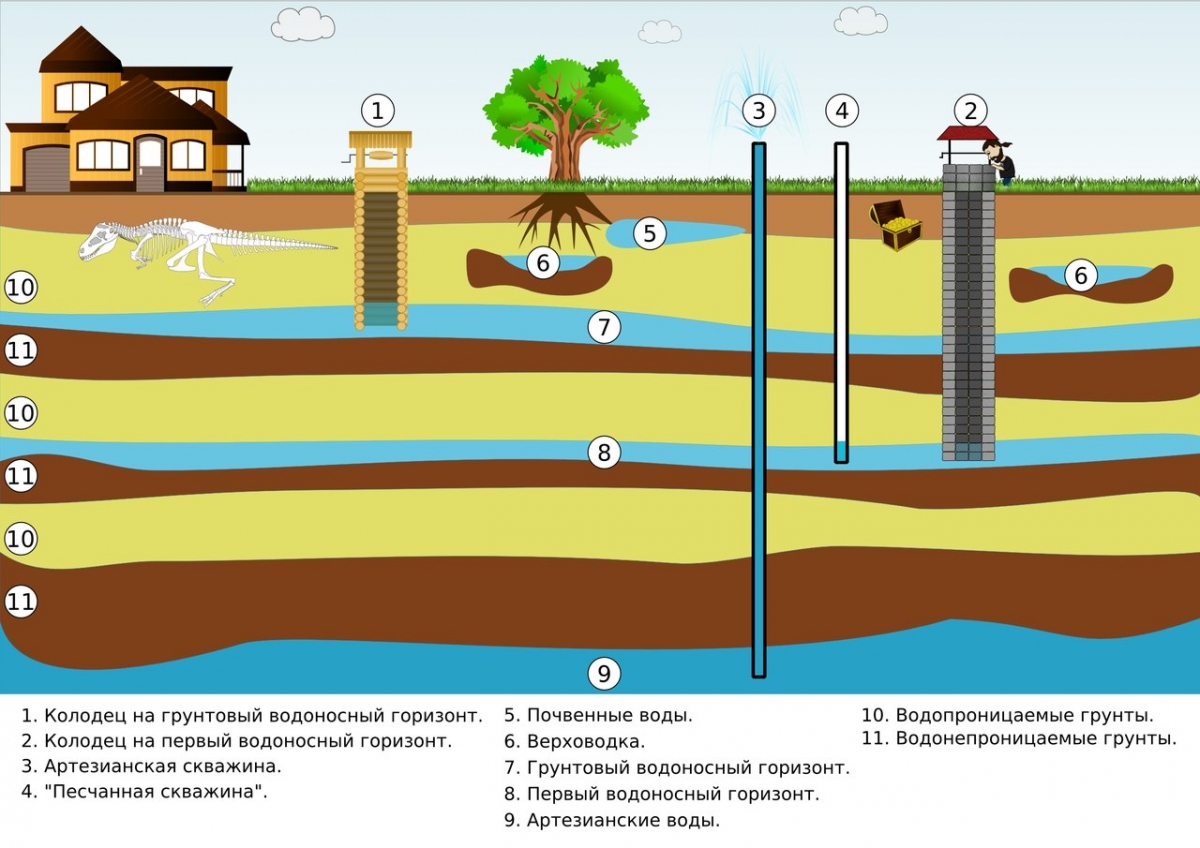
Water intake facilities
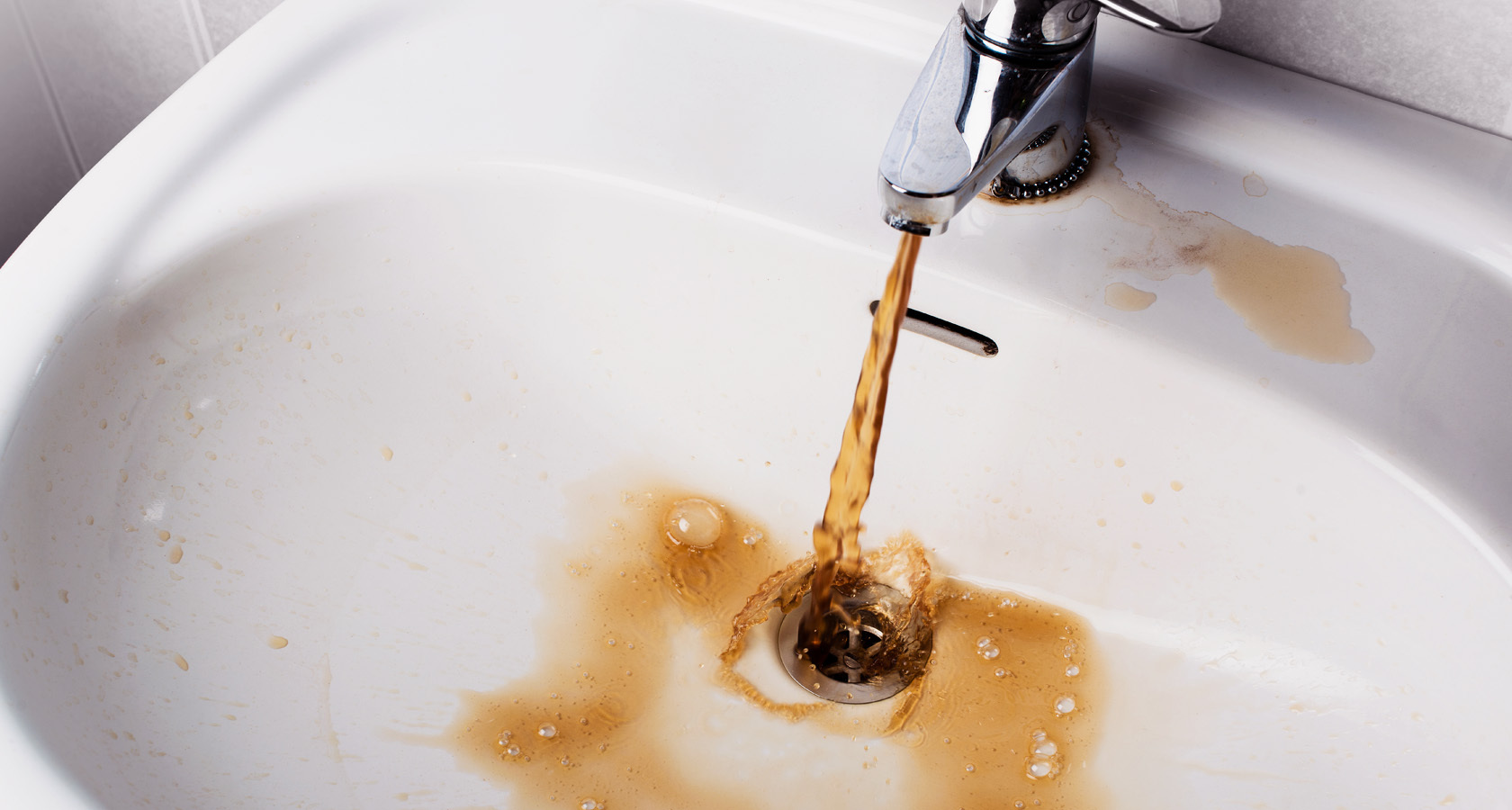
If, for some reason, the water quality has changed for the worse, dispatchers must notify the district or city authorities about this.
Much attention is paid to the treatment facilities of the water supply system. They provide the required degree of purification of the water supplied to the water supply system. Different filtration methods are used here, different types of technologies, equipment and substances are used: drum-type mesh filters, reagent shops, clarifiers and clarifiers, disinfectants, iron removers and other equipment.