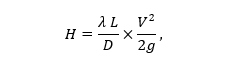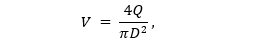Water supply and sewerage are included in the arrangement of buildings and structures where a person lives, rests and works. Installation of water supply and wastewater networks is carried out according to individual projects.
How is the design of water supply and sewerage
The design of water supply and sewerage systems is carried out in stages. Collect initial information about the object: master plan with communications, geological characteristics, technical conditions. Based on the data received, a technical task is formed and a project is drawn up.
Project development solves the following tasks:
- Calculation of water consumption, required water pressure, waste volume.
- Drawing up a plan for water supply and sewerage.
- Selection of materials and equipment.
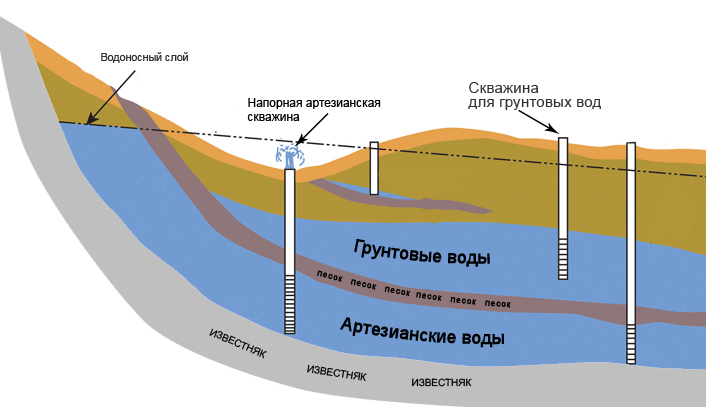
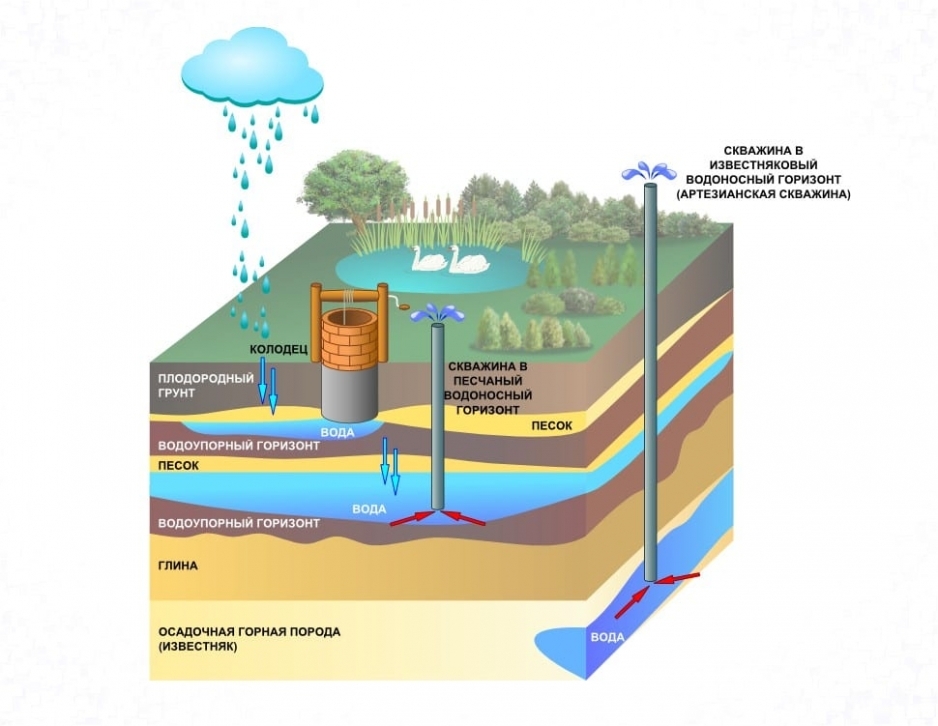
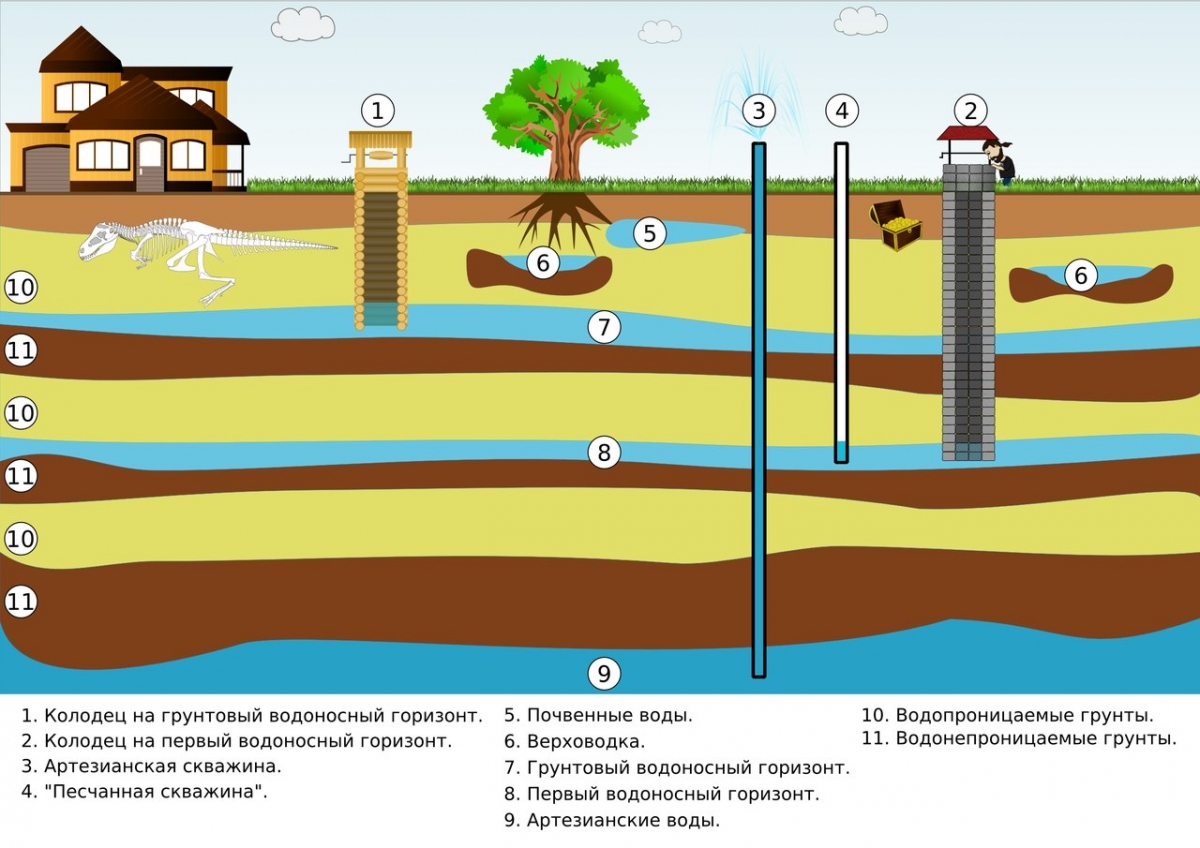
First, the source of drinking water is determined: a central water supply system, a well or a well. If the city networks are not connected, choose a suitable method of obtaining hot water: heat exchanger, electric water heater or gas boiler.
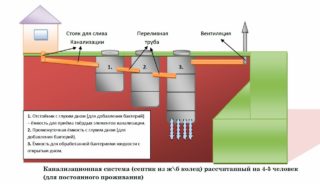
Assign the installation site of the septic tank if there is no connection to the general sewage system. The septic tank is designed at a distance of 30 m from the well, and the main sewer riser is located at the wall closest to it. An external plan of water supply and sewerage is drawn up to the point of entry into the foundation of the building.
Draw up a drawing of the internal wiring of water and drain pipes indicating the lengths, diameters, installation points of plumbing equipment. Projects for wiring networks of multi-storey objects are performed on one or more vertical risers.
The number of plumbing fixtures and users determines the required head, water consumption, drain volume. These characteristics are calculated, the diameters of the pipelines, the parameters of the pumping station are set.
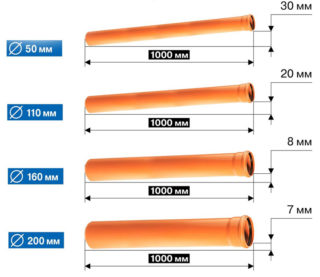
The diameter of the main outer drain pipe determines the slope angle:
- Ø 110 mm - 0.02
- Ø 160 mm - 0.008
It is not allowed to decrease and increase the slope angle of the drain, since the transporting capacity of the liquid is maximum if the calculated value is observed.
The choice of materials and equipment is the final stage in the design of water supply and sewerage systems. Materials are selected taking into account the operating conditions, network load, price limitation.
The architects include in the project the possibility of modernization, expansion, renovation of the complex in the future. This allows you to eliminate breakdowns and install new equipment during operation without unnecessary costs.
The finished water supply and sewerage project contains floor drawings, an explanatory note with calculations, a bill of materials.
What is regulated by SNiP in the design of utilities
Water supply and wastewater disposal is designed based on SNiP 2.04.01-85. The regulatory document prescribes a set of rules according to which plans for water supply and sewerage are developed for residential buildings, public buildings, industrial enterprises. Local treatment facilities are designed in accordance with SNiP 2.04.03-85, taking into account the construction standards of regional departments.
Waste pipelines are laid in a straight line with a given slope, which is not allowed to change.Connecting devices and changing the direction of pipes are made by connecting elements that have a smooth, streamlined angle of rotation.
There are two options for arranging the internal sewage system:
- Open fastening of pipes to walls, supports, ceilings.
- Concealed installation in ducts, shafts, floor structures, ceilings, wall slots with subsequent sealing.
Internal pipelines are protected from mechanical damage, while external ones are insulated and buried under the ground to the design depth. Sewer risers are led out to the roof of the building or to a prefabricated exhaust shaft for ventilation.
Clean-ups are designed in places where drains turn, on dead-end areas, on risers. In multi-storey buildings, riser revisions are installed on the upper and lower floors, as well as on the floors above the indentations. In houses with a height of 5 floors, revisions are made through 3 floors.
SNiP 2.04.01-85 document regulates the observance of additional rules in the design of water supply and sewerage systems in buildings that are built in special climatic and natural regions. These include permafrost and subsidence soils, as well as seismically hazardous and undermined areas.
Compliance with building codes during design will protect the system from possible breakdowns and incorrect operation in the future.
Carrying out the necessary calculations
The design of water supply and sewerage systems includes calculations of the water supply pressure, water consumption, wastewater volume, as well as estimates of material costs. Calculations are reasonable for multi-storey buildings. In small one-story buildings, standard solutions are used.
The calculation of water supply is carried out to determine the water pressure on plumbing fixtures. If the pressure is insufficient, changes are made to the water supply plan: the pump power is increased, the diameter and length of the pipes are changed.
The loss of water pressure as a result of selection by consumers and ascent to the upper floors is calculated by the formula:
Where:
- H - head loss (m),
- λ is the coefficient of friction indicated in the pipe marking,
- L - line length (m),
- D - pipeline diameter (m),
- g - constant: 9.81 m / s2,
- V is the speed of water flow (m / s).
Formula for determining the speed of water flow:
Where:
- D is the inner diameter of the pipe,
- π - constant: 3.14,
- Q - water consumption (m3 / s), taken according to Appendix 2 SNiP 2.04.01-85.
Water consumption depends on the number of residents and the type of equipment installed. The values for different devices and their dependence on the number of water consumers are indicated in the tables of SNiP 2.04.01-85.
The hydraulic calculation of drainage with a diameter of up to 500 mm is made according to the nomogram of Appendix 9 SNiP 2.04.01-85, and for large diameters SNiP 2.04.03-85 is guided.
Complex technical calculations should be entrusted to design engineers. Experts will not make mistakes when drawing up a project, which guarantees trouble-free operation of communications.
Choice of materials

The water supply and sewerage project includes the selection of pipelines with the required parameters. The industry produces a wide range of pipes for drinking water and waste liquids.
Pipeline materials:
- metal-plastic,
- cast iron,
- steel,
- copper,
- polyethylene,
- polypropylene,
- polyvinyl chloride,
- fiberglass,
- asbestos,
- reinforced concrete.
The most widespread are products made of polymers, metal-plastic, stainless steel. Internal water pipes are made of PPRC polypropylene, metal-plastic, PEX, corrugated stainless steel. Internal downpipes are made of PP, gray PVC and HDPE.
For external water supply systems, products made of PE and polyethylene with a protective PE-RC layer are used. External drains are made of orange polyvinyl chloride, corrugated polyethylene and corrugated two-layer PP.
The designer accepts the type of pipes, based on the technical conditions of the project, the advantages, disadvantages of the material, and also takes into account the wishes of the customer.
Stages and features of the arrangement of water supply and sewerage networks
Install a water source: a pump, an autonomous water supply station. Water purification filters are installed. A septic tank or bio-purification plant is being built. An alternative option for giving is a storage tank or a cesspool.
Dig trenches for external water supply and sewerage lines. They fill the bottom of the trenches with sand, put insulation on the pipelines, and lay them with a given slope. The drain into the hole of the non-settled septic tank is set freely until it settles. Lines are brought to the building, connected to the internal network.
Water pipelines are susceptible to freezing in winter, so they are laid below the depth of soil freezing. The best option is that the well and the pump are located inside the outbuilding, then there is no need for external water pipes.
Internal horizontal pipelines of the first level lead from the entry point with a constant slope towards it. On the next floors, a slope is made to the place where the line meets the riser.
Instrument wiring is done using fittings. The turns of the lines are performed with corner fittings. Risers are installed vertically with a ventilation outlet on the roof.
The final stage is testing and final debugging of networks. They supply water, examine the lines with devices for leaks. Eliminate faults if necessary. If there are no shortcomings, then the internal pipelines are closed or sealed, and the external ones are covered with soil.
Concealed pipelines are closed after a special inspection. Water is supplied to them under excess pressure, which is kept for several hours.
The design of water supply and sewerage networks is inextricably linked with the construction of facilities where people are present. The reliability of communications depends on the accuracy of the project.