An aquifer allows you to organize an autonomous water supply for residential buildings. The main stage of the hydraulic structure is the organization of a sanitary protection zone around the drinking water well. It helps to provide protection against bacterial and chemical contaminants.
Design of protection zones
When designing a ZZO and establishing its value, it is envisaged to carry out general works to protect the territory from polluting factors. In this case, the following data are taken into account:
- water lifting method;
- the productivity of the intake structure;
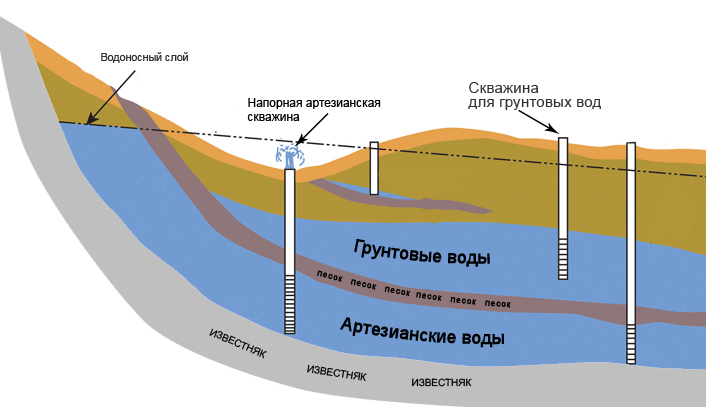
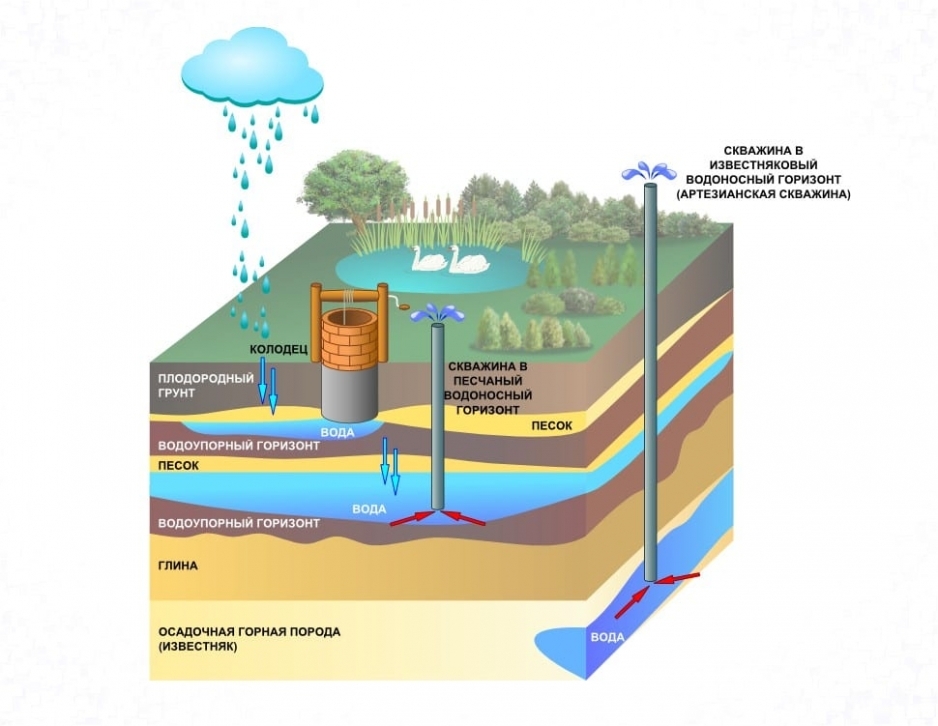
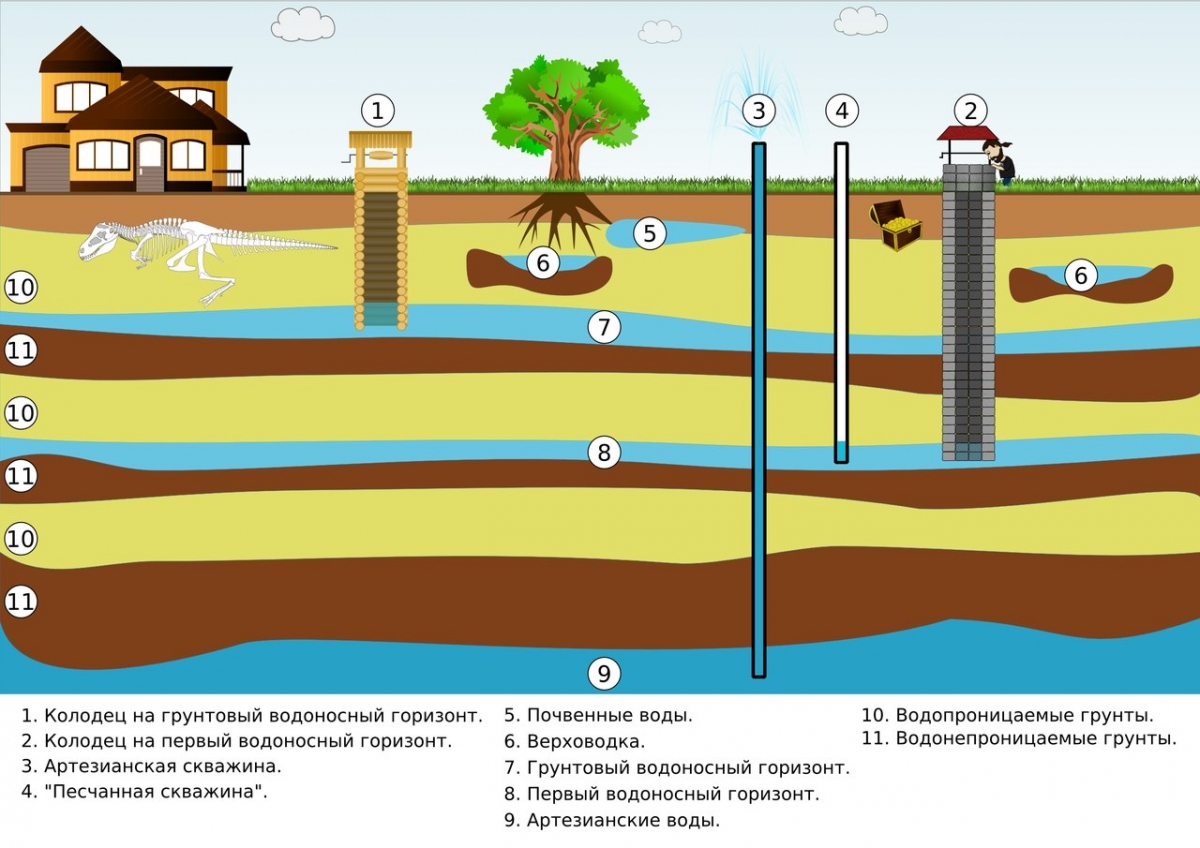
- the depth of the aquifers;
- distance from a septic tank or cesspool.
The protective space is organized by taking into account the data of various studies. They include the study of the microbiological environment, indicators of the aquifer. When arranging a well and creating a project for a protected area, coordination with the authorities of sanitary-epidemic and housing control is required.
Belts and boundary definition
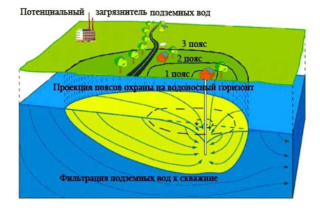
First belt
The dimensions depend on the availability of waterproof protection. If it is present, the radius from the water source located in the center is 30 m, in the absence - 50 m. Various water supply installations are located here. They are equipped with devices that prevent contamination of the liquid through the pipeline.
In the first belt it is prohibited:
- construction, installation and restoration works;
- construction of technical structures that are not related to the processing and supply of liquid;
- construction of buildings and structures, even garden pavilions;
- laying of pipelines, except for pipes for servicing hydraulic structures;
- discharge of drains, bathing, washing, fishing, grazing livestock.
The diameter can be reduced to 20 meters if the hydraulic structure has high sanitary and technical indicators, and the aquifer has reliable protection from polluting factors. A warning sign must be posted at the border of the first belt.
Second belt
Equipped to protect the hydraulic structure from bacterial pollution. The diameter of the section is determined individually and can be:
- up to 500 meters - on plains;
- from 700 meters - in mountainous and hilly areas;
- from 950 meters - on hilly areas, areas with uneven relief;
- up to 3 kilometers - in the presence of surface water sources: rivers, lakes, reservoirs.
On this site, it is impossible to equip farms for breeding animals and pastures, landfills for garbage disposal, warehouses for substances with chemical activity. There should be no cemeteries, cattle burial grounds, sites for sewage disposal, filtration and irrigation, silo pits.
Third belt
The protective zone of the water intake well of the third belt implies the coverage of the territory to prevent the ingress of chemical pollutants into the well and the aquifer. The location of objects that lead to contamination with chemical, toxic and other hazardous substances is not allowed here.
You cannot equip here:
- chemical industry facilities;
- warehouses for chemicals, fertilizers and fuels and lubricants;
- accumulators of sludge and waste liquids for industrial purposes;
- harmful production.
The size of the zone is determined individually for each type of aquifer. The calculation of the diameter of the sanitary area is carried out taking into account the time interval required for the penetration of bacterial and chemical pollutants into the water intake point.
Zones of sanitary protection of hydraulic structures do not have definite operational periods, if the basic requirements for the operation of wells are adhered to. They are capable of functioning for at least 30 years without additional purification.
Measures to eliminate pollution factors
- drainage of storm water from walking areas and other areas where animals and birds are located, with their collection into waterproof storage tanks for storm water;
- additional waterproofing of the foundation and floors in industrial buildings located nearby;
- installation of reservoir and linear drainage systems that collect filtered water and solutions for pumping and further purification;
- the use of crushed stone filtration layers with a network of drainage pipes that remove contaminated wastewater;
- contraction of the contour of polluted fluids of aquifers into a depression funnel through special drainage wells or ditches.
Analyzes of the biological and chemical parameters of water sources and soil structure are carried out in order to accurately determine the appropriate protection methods.
Measures for the arrangement of the well and the creation of the project must be coordinated simultaneously with the working project for the water supply of the site.
Regulatory documents and liability for non-compliance
All norms for the organization of water protection zones are stipulated in SanPiN 2.14.1110-02. The project of the WSS wells for drinking and industrial water is being developed by specialized organizations, based on the hydrogeological conclusion on the territory where the structures for hydraulic engineering are installed. It can be formed at the stage of drilling a foundation pit or created specifically for an existing structure. The technical documentation is coordinated with the sanitary and epidemiological supervision and housing control authorities.
An appeal to the regulatory authorities for a new opinion is required in the following cases:
- the owner of the water intake point has changed;
- there have been changes in the boundaries of the land plot, the scheme of using water intakes;
- the amount of water used per day has increased;
- decreased organoleptic values.
The conclusion is also necessary when plugging an old well or well.
In accordance with the current legislation, penalties are provided for violation of the rules for the use of water sources and wells, non-compliance with sanitary standards. Fines, depending on the degree of violation of regulations, can reach half a million rubles. On average, they amount to 30,000 rubles. The perpetrators of serious pollution face criminal liability, which includes arrest for a term of three months to five years.
The creation of protected areas is necessary to preserve the integrity of the well or well, protect the soil structure, and prevent contamination of the water-containing layer. When constructing buildings in the second and third zones, one must be guided by sanitary standards and SNiPs. Such strict requirements will avoid massive epidemics and further environmental pollution.