Centralized water supply consists of an infrastructure complex of intake stations and treatment facilities, distribution networks and pipelines. The health and life expectancy of people depend on the quality of the water used, therefore, the SanPiN for water supply was developed, which defines the hygienic standards of safe characteristics for tap drinking water.
SanPiN for centralized water supply
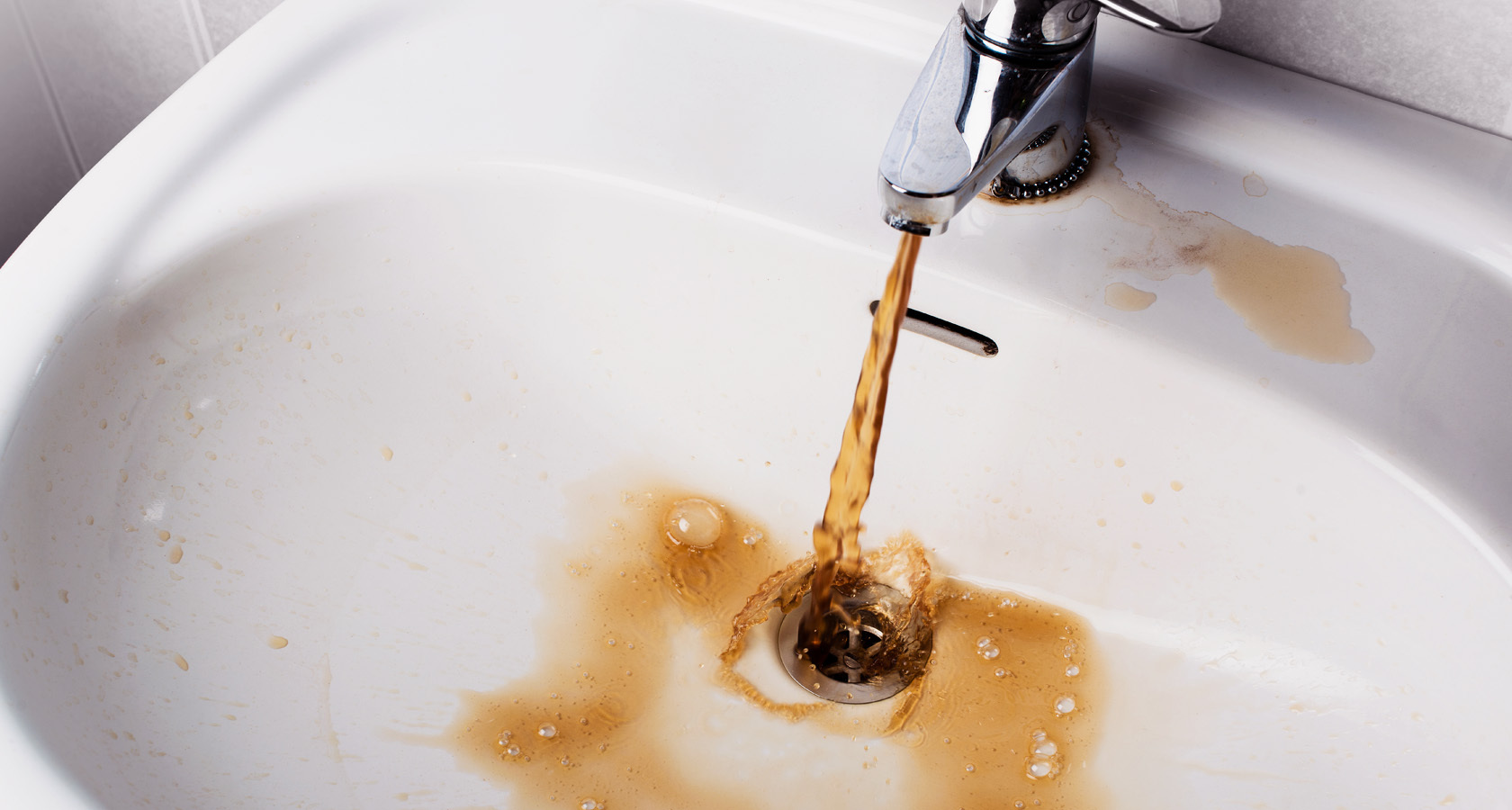
Water bodies can contain dangerous viral, zoonotic and infectious pathogens, eggs of helminths and biohelminths. In some regions, the excess or lack of minerals in the soil leads to endemic diseases. Due to the ingress of toxic industrial effluents into water sources, chronic intoxication of people is possible. Compliance with the hygienic requirements of SanPiN and quality control of drinking water ensures a safe water supply.
Scope and general provisions
SanPiN of centralized drinking water supply refers to the activities of organizations and individual entrepreneurs supplying settlements with drinking water, performing design work, construction and operation of water supply systems. State bodies use standards for sanitary and epidemiological control. The SanPiN requirements apply to the water supply of the population, factories engaged in the processing of food raw materials, the manufacture or storage of food products, to trade organizations, to other industries that require drinking-quality water.
According to SanPiN, the water quality of centralized water supply must be strictly controlled in accordance with the standards. In case of inconsistency of laboratory samples, in situations that deteriorate the quality of water, and other deviations, companies should immediately report this to the sanitary and epidemiological station and begin to eliminate the violations.
If the consequences of natural disasters and serious accidents cannot be quickly eliminated, temporary deviations from the specified chemical composition are possible, coordinated with the sanitary and epidemiological supervision. In this case, several conditions must be met:
- the population cannot be provided with water in other ways;
- deviations are introduced for a limited period of time;
- the timeframe for violation of standards was reduced as much as possible;
- absence of threats to the health of citizens;
- informing the population about water quality, introduced deviations, their duration and possible health risks.
According to SanPiN, centralized water supply can be suspended if the causes of the accident are not eliminated and the hygienic characteristics violate the standards. When it is not possible to provide a safe water supply, the rules call for a complete ban on the use of the water supply and for providing residents with water in other ways.
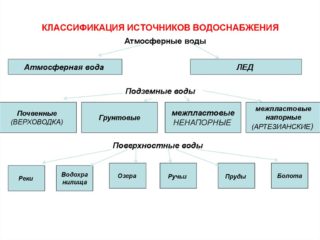
Sources of centralized water supply
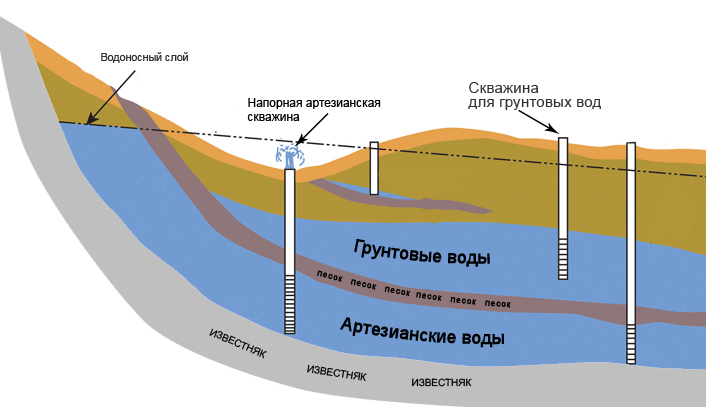
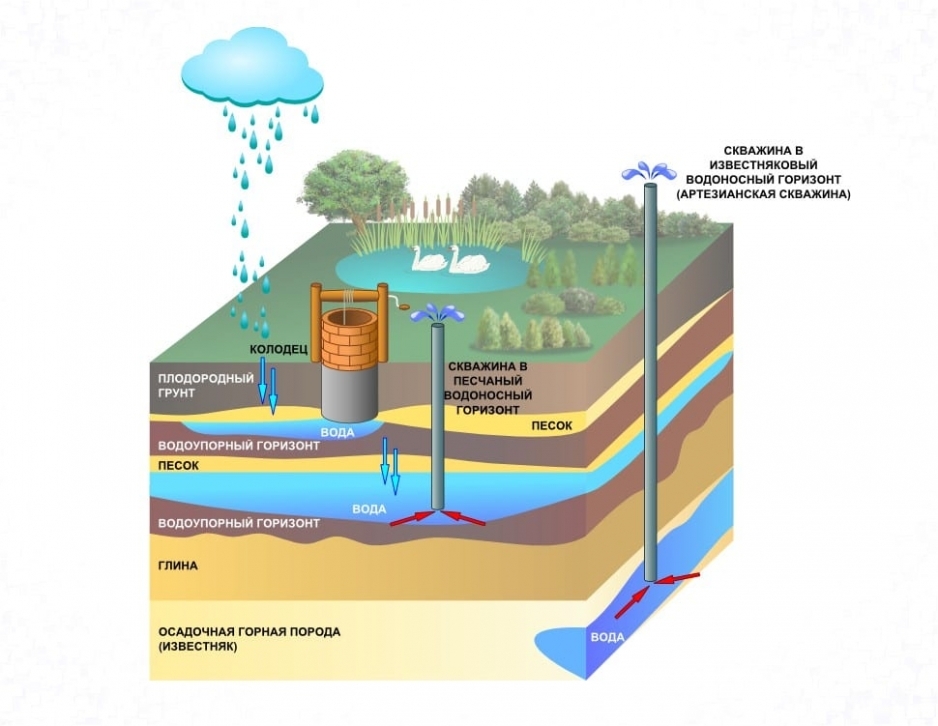
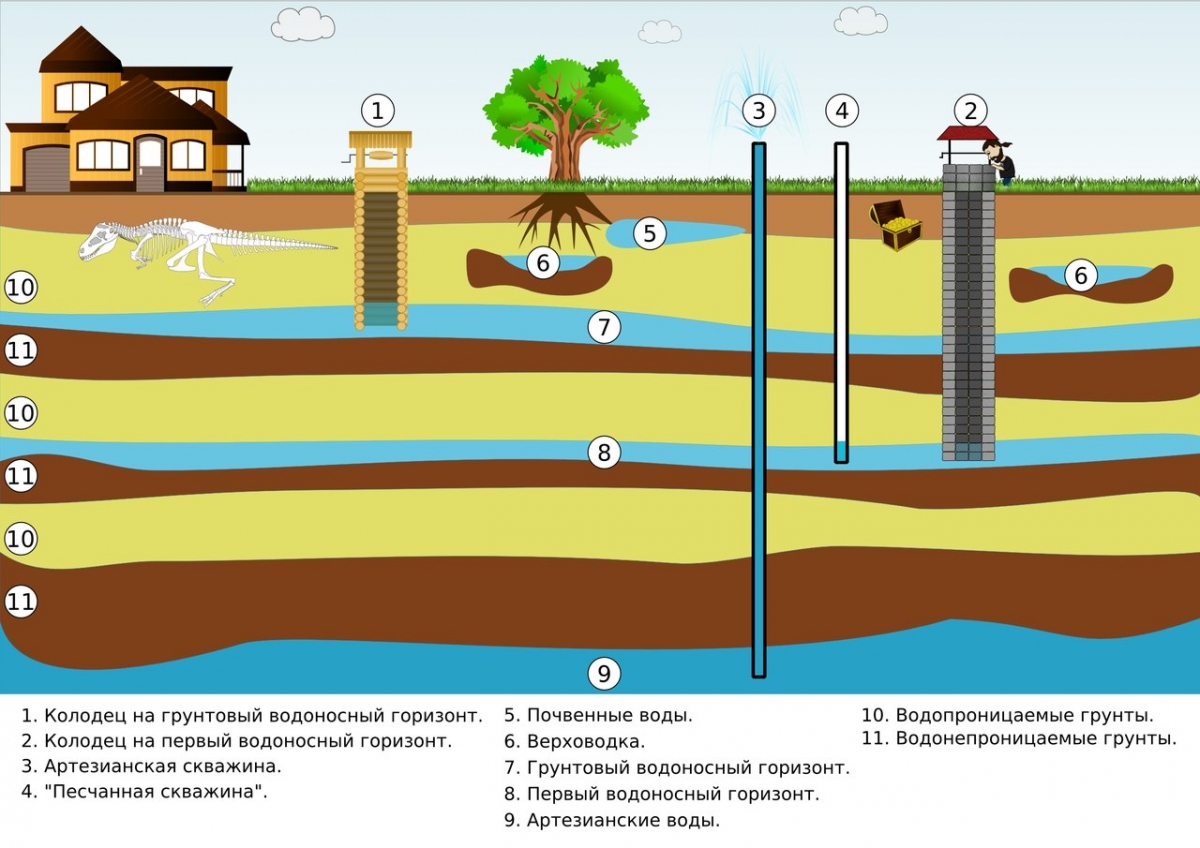
- Underground. Interstratal waters can be consumed without sanitization. Groundwater does not have an upper waterproof layer; it is much inferior to interstratal sources in terms of hygienic characteristics.SanPiN permits their use for water supply only in small settlements.
- Open ground sources - rivers, canals, lakes, reservoirs. They require cleaning and additional processing. They are characterized by the presence of suspended particles, increased mineralization, bacterial contamination, seasonal fluctuations in chemical substances. Often contaminated with toxic substances.
- Atmospheric sources. They also require decontamination and cleaning. They are characterized by reduced mineralization, high content of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and bacterial contamination. Their chemical composition depends on atmospheric pollution.
According to SanPin, water from centralized water supply sources is regularly checked for compliance with the requirements. To prevent the ingress of toxic substances into water sources, increased requirements have been established for the protection of the water intake. It is forbidden to have warehouses with pesticides and fuels and lubricants, cemeteries and cattle burial grounds in the security zone.
Hygiene requirements and standards
- harmless chemical composition;
- favorable organoleptic properties;
- epidemiological safety;
- compliance with radiation standards.
The epidemiological component is controlled by parasitological and microbiological tests. The presence of coliform bacteria, lamblia cysts, coliphages, spores of sulfite-reducing clostridia is not allowed. The total number of microbes is less than 50 in 1 ml of water. Violation of these norms can lead to an epidemiological threat to the population. Therefore, in the catering sector, in hospitals, schools and preschool institutions, supervisory services strictly monitor the quality of the water supply.
- according to generalized indicators, the hydrogen content rate is no more than 9;
- hardness not higher than 7-10 mmol / dm3;
- oxidizability with permanganate is not more than 7;
- dry residue of total mineralization up to 1500 g / liter.
Water with a dry residue of 1000 mg / dm3 is considered fresh; more than 1000 mg / dm3 mineralized.
The content of oil products, surfactants and phenols should not exceed the standards. The presence of organic matter is unacceptable. Strict control of the level of extremely hazardous, highly hazardous, hazardous and moderately hazardous inorganic substances.
After treatment with harmful chemicals, it is necessary to control the content of residual chlorine and polyphosphates. After chlorination, the level of chloroform is checked, and during ozonation of formaldehyde. Sanitary and epidemiological supervision in some cases allows increasing the concentration of chlorine.
Organoleptic characteristics depend on the chemical composition. Water of good quality has a color value of at least 20, turbidity up to 1.5-2 mg / dm3, transparency more than 30 cm. Taste and smell are not felt or are very weak. If they are noticeably pronounced, this indicates insufficient cleaning. There should be no film or aquatic organisms visible to the naked eye.
Radiation safety is monitored by indicators of total alpha and beta activity, the presence of radon and some radionuclides. For underground sources, usually no treatment is required, but a radon test is mandatory.
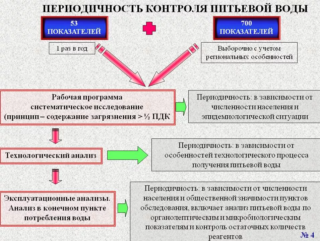
Drinking water quality control
Before entering the network, the liquid must be checked for all indicators.Organizations of distribution water supply networks are obliged to regularly monitor the quality of drinking water in accordance with SanPiN standards with the following frequency per month:
- when servicing up to 10 thousand people - 2 times;
- up to 20 thousand people - 10 times;
- up to 50 thousand people - 30 times;
- up to 100 thousand people - 100 times;
- more than 100 thousand people - 100 + 1 sample for every 5 thousand people.
The company must notify the sanitary and epidemiological station about all deviations from the specified parameters. For violation of control rules and non-compliance with the hygienic characteristics of water, the guilty organization is fined. The revealed violations must be corrected as soon as possible.
Serious attention is paid to water supply control. Disinfection and treatment make it possible to supply the population with high-quality tap water and drink it without fear.