A set of rules or "joint venture" for an internal water supply and sewerage system is a document that includes rules for the installation, maintenance and operation of designated utilities. In construction during the construction of communication systems, this document is considered fundamental.
Basic Provisions
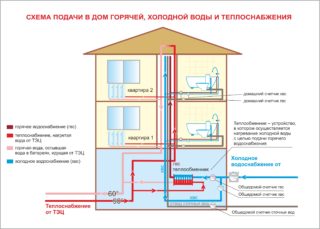
The internal section of the water supply and sewerage system is connected to plumbing fixtures, and on the other side to external networks. On the one hand, the outer section is connected to the inner circuit, on the other - to centralized networks. If the sewage system is autonomous, it is connected to a septic tank, the water supply system is connected to a pump.
The SNiP clearly states that water supply and sewerage networks must be installed in all buildings, regardless of purpose, number of storeys, occupied area. If the centralized sewage systems are located far from the structures being built, cesspools, backlash closets and other similar structures are built. There are special requirements for them in the set of rules.
Water characteristics
The water transported through the pipelines must comply with the requirements that are determined by SNiPs. If it is cold water supply, GOST number 2874-82 and under the name “Drinking water. Hygienic Requirements and Quality Control ”. If water is used for technical needs, each consumer develops his own technical conditions. At the same time, water treatment systems must be installed at plants and factories, which will bring the quality of the liquid to the required one, indicated in the TU.
Hot water supply is mainly determined by temperature.
- For residential and non-residential buildings - 50-70C.
- For children's institutions - below 37C.
The quality of water in sewer networks is determined by the amount of sewage entering it.
Plumbing system
Cold water
Clause 4.1 of SNiP clearly states which parts the internal water supply should consist of. It includes:
- Piping connected through the wall or foundation of the building to the outside of the system.
- Water metering units, which include water consumption meters, shut-off valves, places for taking water samples for analysis.
- Distribution system for consumers (plumbing fixtures).
- Risers located between the floors of the building.
- Shut-off valves. This applies not only to plumbing fixtures, but also to shut-off valves or valves.
In some cases, one or more tanks are added to create a water supply, as well as pumping units.
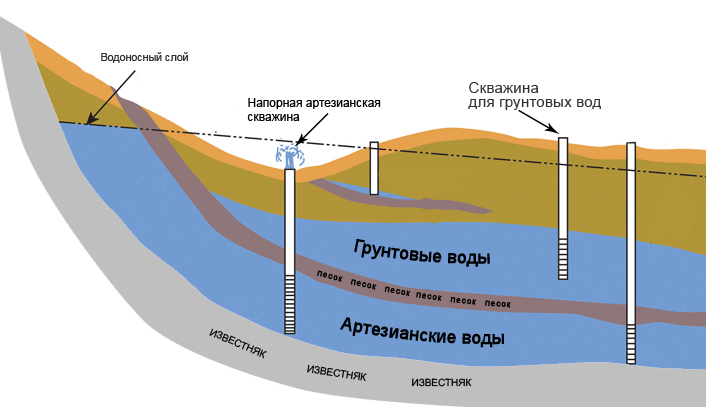
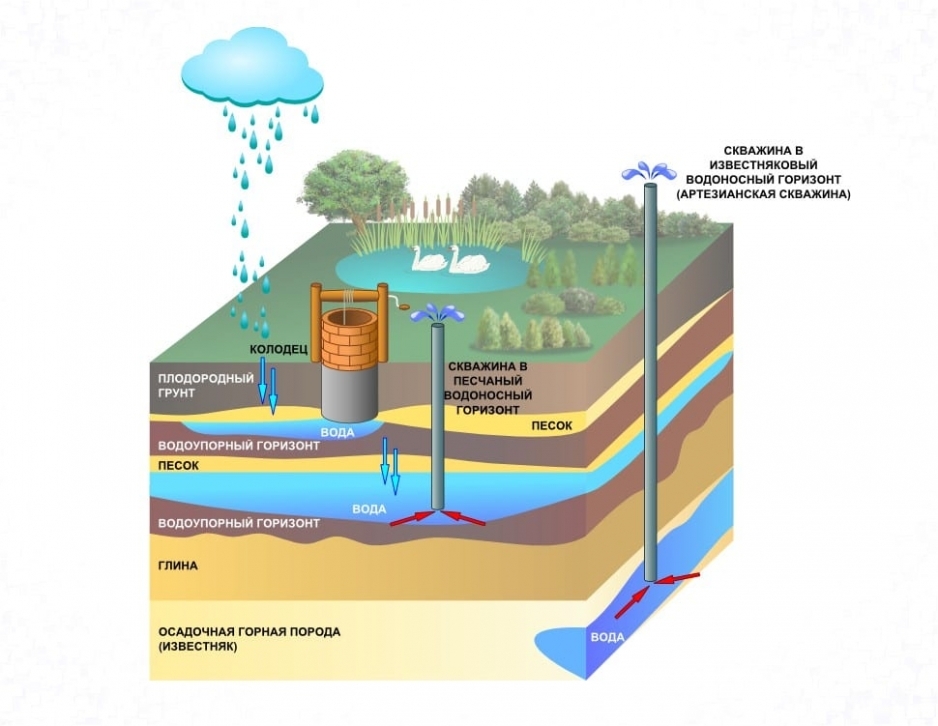
An external water supply is basically a pipe structure connected to a central water supply network. In a stand-alone system, it is connected to a pump. The main requirement for this part is heat and waterproofing. The first makes it possible not to bury the pipes below the level of soil freezing. The second provides protection against the negative effects of moisture.
Clause 4.4 describes the requirements for the installation and maintenance of the water supply system. There are two main requirements:
- So that the components of the plumbing system do not quickly fail, they are selected from materials that can resist the negative effects of water for a long time, as well as moisture from the outside.
- Depending on the technical condition, the entire network must be subject to prevention, inspection, maintenance and repair.
Fire-fighting water supply is classified as "cold". It can be connected to the drinking water supply or technical water supply, if the latter is provided at the facility.
It is strictly forbidden to combine water supply sections of cold water supply of an economic type or drinking water supply with industrial ones.
Hot water
This is the most complex water supply system. The SNiP (specifically paragraph 5) describes the terms and conditions for the use and installation of a hot water supply system. Here are some important points:
- It is impossible to combine in one system the hot water supply system used for household needs with the industrial water supply network.
- If, according to technical conditions, hot water can be supplied simultaneously for both household and industrial needs, the water supply can be laid in one pipe.
- If the building is more than four stories high, the risers should be combined into one unit with one pipe installed. The standard combination is 3-7 risers in one.
- In buildings with a height of less than four floors, it is prohibited to connect water intake devices directly to the risers of the system.
- The installation of the hot water supply system in the villages is carried out taking into account the economic side of the matter, the capabilities of consumers and the technical procedure for carrying out the work.
Hot and cold water supply systems are equipped with drain devices that are installed at the lowest point. As well as devices with which air is released. They are located at the highest point.
Plumbing engineering equipment
The component that takes up the most space is the pipe. It is laid from the central water supply to consumers. In the masses of connection, a water meter is installed, which is cut off on both sides by valves or valves. The system also uses a variety of fittings to help guide piping. A shut-off valve must be installed in front of each consumer.
The water supply system may include water treatment. This is a complex of filtering devices that purify water, disinfect, fill it with useful substances and minerals. In private housing construction, tanks are additionally installed for storing water supplies, as well as alluvial equipment that pumps liquid from wells or wells into the house.
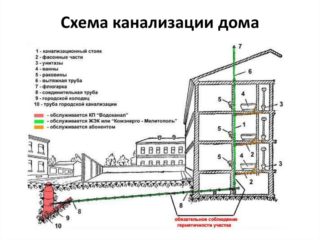
Sewerage systems
- Household sewerage system. Accordingly, it is constructed in residential buildings.
- Production. It is installed to drain wastewater from various types of production workshops.
- United. Combines the two previous varieties.
- Drains. Their task is to divert rain and melt water from the roofs of buildings and structures.
On the territory of industrial enterprises, all four types of sewer networks are often combined into one, if special technical devices are installed in them:
- hydraulic locks, which are installed on each sewer site and provide sanitary and hygienic standards for the operation of the sewage system;
- grit traps in storm sewers that trap debris and sand.
SNiP does not strictly stipulate what type of system can be installed indoors: open or closed. The second is more often used, but the first can also be mounted, if this is confirmed by technical standards.For example, if non-toxic, odorless wastewater is transported. In this case, the open-type sewage system must be equipped with hydraulic locks.
Standard sewerage systems, especially internal ones, are gravity-fed. Therefore, it is laid at a certain angle from the buildings towards the water intake. This technical parameter depends on the diameter of the laid pipes and varies in the range of 2-5 mm per one running meter of the pipeline length.
Inside buildings, the sewer network can be laid in an open or closed way. In the first case, these are pipes laid along the surfaces of the supporting structure of the object: walls, floor, ceiling, columns, etc. In the second case, this is a pipe wiring recessed into the same building structure. For this, grooves (grooves) are made, into which pipe products are laid and covered with repair mixtures (plaster, putty), plate or sheet materials.
External sewerage is laid directly into the ground, for which it is isolated, or in pre-assembled tunnels, pipes of larger diameter, trays and other building elements intended for laying utility networks. Here, the angle of inclination of the pipe is also compulsorily maintained for the gravity movement of wastewater.
A pressure sewage system differs from a gravity one in that it contains a pump. It pumps drains and sewage forcibly. This type is used only if it is not possible to lay sewer pipes at an angle. The pump can pump wastewater not only horizontally, but also obliquely from bottom to top. This type does not differ in energy saving, but under certain circumstances there is no other way out.
There is one most important point in the joint venture: the water supply network cannot be laid next to other engineering systems. The exception is the highways along which non-toxic materials are transported.