Construction rules and regulations for an external water supply system regulate the installation and operation of water pipes that supply water to residential buildings and industrial facilities. The SNiP also indicates the design characteristics of components for the assembly of such networks.
Updated edition of SNiP 2. 04.02–84 as amended
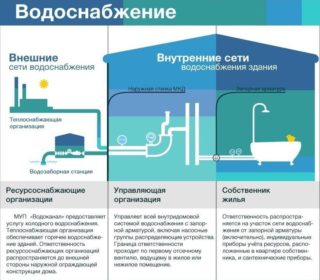
SNiP under the term "external water supply" means highways passing outside buildings.
First of all, the set of regulatory documents indicates the requirements for the quality of the incoming fluid:
- The water supplied from the central water supply network and allowing to ensure the conduct of household activities, as well as used for drinking, must meet the quality standards that are regulated by GOST and SanPiN.
- Determination of the quality of liquid for the needs of industrial premises depends on the technological standards of the enterprise.
- If it is planned to use water for irrigation of green spaces, it must meet sanitary and agricultural standards.
The standards list the types of pipes that are allowed to be used for the assembly of external water supply systems. The list is quite long. In practice, polyethylene pipes are mainly used for external cold water supply lines. They combine such qualities as a long service life, low hydraulic resistance, resistance to clogging by deposits and flexibility, which allows the main water supply to withstand subsidence and movement of the soil.
The procedure for calculating the daily use of water by one tenant for houses of different types is also spelled out:
- with internal cold water supply pipeline and without baths - 125–160 liters;
- with autonomous water heating devices and baths - 160-230 liters;
- with baths and a central hot water supply system - 220-280 liters.
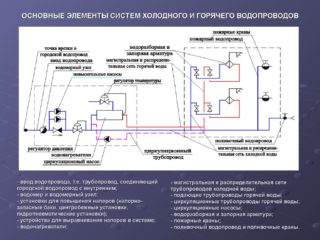
The head at the entrance to a one-story house must be at least 10 meters. For each subsequent floor of the building, you need to increase the indicator by 4 meters. The temperature range in the DHW network should be 60–75 degrees, regardless of the type of water supply system.
An air vent is installed at the top of the jumper between the risers of the DHW circulation system. At the lowest points of all risers, the installation of dump valves, plugs or water fittings is required.
When hot and cold water supply pipelines are introduced into a house or apartment, non-return valves are mounted on metering units for its consumption. They prevent the counter from moving in the opposite direction. Without them, in order to wind up the readings, you can apply the difference in pressures on the cold water and hot water supply.
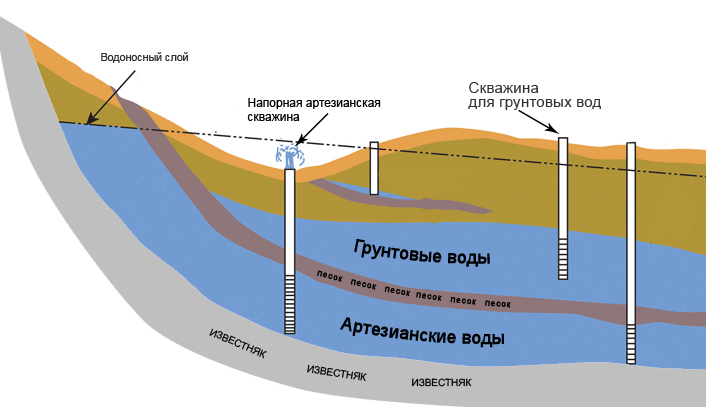
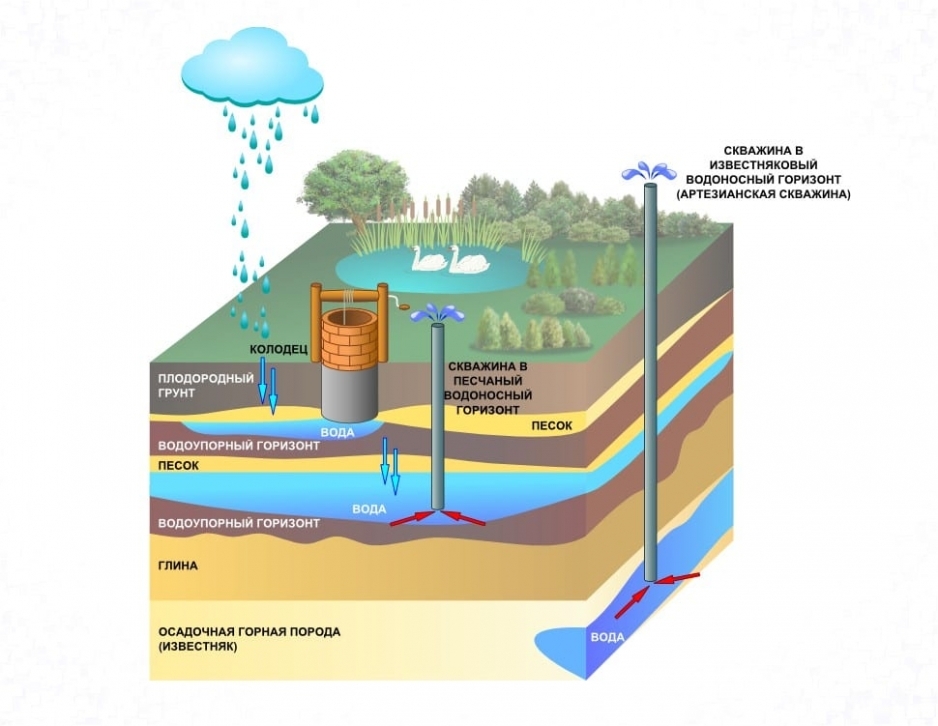
The requirements for the construction of wells and wells, the minimum distances to the main sewerage networks and other communications, the peculiarities of joint economic and fire-fighting water supply are also written in the normative act.
SP 31. 13330. 2012 - the current edition of SNiP 2.04.02–84 carries certain changes. They update the previous code of practice.
New moments
The general rules have been amended.They concerned, in particular, the use of water pipes made of various materials:
- Siphon and gravity water conduits are made of durable steel or cast iron pipes, but it is allowed to use pipelines made of plastic and reinforced concrete.
- All lines, except for those made of reinforced concrete, are tested for ascent.
- Metal pipelines are equipped with anti-corrosion insulation. Made of steel - cathodic or protective protection.
In addition, it is indicated that water lines made of glass-composite pipes with threaded connections, as well as blocking joints of the coupling and socket type, do not require the installation of concrete stops.
Accurate test pressures are given. For simple cast-iron pipelines, its coefficient in relation to the internal design head is 1.5, for steel and high-strength cast-iron pipes - 1.25, for polymer systems - 1.3.
Also, the new chapters describe the requirements for the installation of expansion joints, which will protect the joints of the branches from destruction, and the types of soil for the correct laying of highways.
Normative references
The normative act is based on the laws and regulations given in other documents. The most significant of them are:
- SP 30.13330.2012 based on SNiP 2.04.01-85. Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings.
- SP 42.13330.2011 based on SNiP 2.07.01-89. Urban planning. Planning and development of urban and rural settlements.
- GOST 25151-82. Water supply. Terms and Definitions.
- GOST 2761-84. Sources of centralized drinking water supply. Hygienic, technical requirements and selection rules.
- SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01. Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control.
- SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02. Zones of sanitary protection of water supply sources and drinking water pipelines.
However, the list is much broader. It includes regulations governing fire protection, building construction, loads on hydraulic structures, state standards for various pipelines and sanitary requirements for water extracted from various sources.
Responsibility for non-compliance with rules and regulations
In certain cases, it is allowed to make changes to the design of the water supply scheme, but in accordance with the standards and regional specifics. To avoid disagreements leading to prosecution for violation of SNiP, it is worth agreeing on a water supply project in advance.
A careful study of regulations and terrain before starting any work will prevent the payment of large fines for any, even careless, damage.
Penalties for legal entities that gave orders to perform work that resulted in breakdowns of communication networks of varying severity are quite large - about 30,000 rubles. For officials, the amount of the fine is about 3,000, and for individuals it will be about 1,500 rubles.
Violation of the standards for the arrangement of the water supply system, which led to serious consequences, may turn into criminal liability.
Following the rules and obtaining a copy of the layout of all engineering networks will help to avoid punishment in the future.