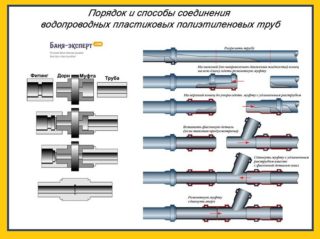
When organizing water supply, pipes made of various polymeric materials are very popular: polypropylene, metal-plastic, low-pressure polyethylene, chlorinated polyvinyl chloride. Their gradual replacement of traditional cast-iron and steel counterparts is associated with their durability, low cost, strength and resistance to adverse environmental factors, ease and convenience of connection. Such advantages make it possible to significantly speed up the process of installing water supply networks, reduce their cost and labor intensity.
Ways to connect water pipes
The method of connecting plastic pipes when installing a water supply system depends on what material they are made of. The methods and tools used for pipelines made of one type of plastic are not applicable for others.
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC)
- A piece of the required length is cut from the whole pipe using a special tool - a pipe cutter.
- The workpiece is assembled with a fitting (angle, tee, coupling) without gluing. In this case, the distance of the pipe that enters the joints is measured.
- A chamfer is removed from the end of the workpiece with a special tool or a sharp knife.
- The outer surface of the workpiece and the inner fitting are degreased using a special solvent.
- A thin layer of a special glue based on liquid chlorinated polyvinyl chloride is evenly applied to degreased surfaces.
- The pipe is connected to the fitting at the required angle and fixed in this position motionless for 1 minute. The glue holds the connected elements of the water supply very quickly and does not require additional efforts to fix them during the gluing process.
- Remains of glue are removed with a sharp knife.
The plastic pipeline assembled in this way operates at high water pressure and does not leak. In case of unintentional damage to the water supply system, it can be quickly and easily repaired - for this, a suitable piece of polyvinyl chloride is inserted into the hole and poured on top with a thin layer of glue.
Pipes made of simple polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with a gray or bright orange color are not used in water supply networks. Their characteristics and the socket type of connection do not allow ensuring the tightness and stability of the water supply system - with a high pressure, they leak. Under the influence of hot water, they begin to deteriorate quickly. Such communications are widely used for laying external and internal sewerage systems.
Metal-plastic
The connection of metal-plastic water pipes is made using crimp and press fittings.

Install the compression fitting as follows:
- Using scissors or a hacksaw, a piece of the required length is cut from the whole pipe.
- A nut and a ferrule of the fitting are put on the cut workpiece.
- With a gauge or a cone-shaped object, the inner diameter of the workpiece slightly expands - it is calibrated. When using a gauge, at the same time, deburring from the end of the workpiece occurs - countersinking.
- The fitting is inserted into the workpiece. To make it easier to enter and prevent scoring and slipping of the sealing rubber rings, it is lubricated with liquid soap.
- At the junction of the fitting and the workpiece, first push the compression ring, and then the nut.
- Fix the fitting in the workpiece by clamping the nut with an adjustable wrench on the thread.
A metal-plastic water pipe made using this technology, a hot or cold water riser will last up to 10-12 years. In this case, the connection is collapsible, it requires periodic inspection (1 time in 3-4 years) and tightening the nut if a leak is detected.
The connection process using press fittings is more laborious and requires special equipment - a manual or electric press. The sequence of fixing press fittings consists of the following manipulations:
- The inner diameter of the pipe section is calibrated and countersinked using a special gauge.
- A press fitting with a crimp sleeve is inserted inside the workpiece. The completeness of the contact between the pipe and the fitting can be judged with the help of special indicator windows on it - if they are completely closed by the pipe, then you can start pressure testing. If not, it is necessary to re-calibrate and countersink the inner diameter of the workpiece more carefully.
- The fitting is fixed on a metal-plastic workpiece using an electric or manual press with nozzles of the appropriate diameter.
Compared to a crimping connection, a crimp connection is more convenient - if a strong leak appears, which cannot be eliminated by tightening the nut, it can be disassembled, the O-rings replaced and quickly assembled. Press fittings, although they do not require periodic inspections and maintenance, cannot be repaired if they leak or become damaged.
Polypropylene

The most common method of joining polypropylene pipes - high-temperature welding - consists of the following steps:
- A workpiece of the required length is cut from the whole pipe.
- The inner surface of the fitting and the outer workpiece, which are connected during brazing, are degreased.
- With the help of a black pencil, clearly visible on a white background, a mark is made on the workpiece, indicating how far the pipe should go into the fitting when soldering.
- The workpiece and the polypropylene fitting are simultaneously inserted into the sleeve and the mandrel on the tip of the soldering iron (apparatus for high-temperature welding of polypropylene products) heated to the required temperature.
- After 5-10 seconds, the parts to be soldered are removed from the working bodies of the soldering iron and connected without rotation.
- Until complete cooling, it is permissible to change the angle of the workpiece and the fitting in a vertical or horizontal plane, without rotating them relative to each other.
When brazing such pipes, it is important to observe the temperature and heating time of the parts to be joined. With prolonged exposure and high temperatures, polypropylene can melt strongly, blocking or narrowing the passage inside the water passage. Insufficient temperature and short exposure will lead to leaks due to incomplete fusion of the connecting surfaces of the fitting and the pipe with each other.
Plumbing products made of polypropylene will poorly join if there are water drops on the surfaces to be soldered - moisture evaporating during soldering will prevent the normal sintering of polypropylene, leading to the formation of cavities and gaps in the soldering seam.
Polyethylene
- The crimp nut is first put on the pipe, then the collet (crimp ring).
- The pipe is inserted into the fitting body until it stops.
- The collet moves towards the threaded part of the fitting.
- The fitting is fixed to the pipe by tightening the nut.
To connect HDPE pipes for a large-diameter water supply system (more than 100 mm), special welding machines are used, which are used to install high-pressure water supply lines. It is impractical to use such a device for the installation of a personal polyethylene water supply system in a private house.
Features of connecting pipes from different materials
In practice, it is often necessary to connect pipes made of materials of different properties: metal and polypropylene, metal and polyethylene, polypropylene and metal-plastic. Fixation methods:
- To connect metal pipes with polypropylene, combined couplings are used, which have an external or internal thread soldered into plastic.
- The connection of a polyethylene (HDPE) pipe with a steel pipe is made using compression couplings. In this case, the polyethylene pipe is fixed in the fitting in the traditional way, and the steel thread is screwed into the sleeve with flax or tow and grease being pre-wound on it with sealing paste. Polyethylene waterways of large diameters will be connected to a gate valve, a cast-iron valve using a special flange and strong bolts.
- The fixation of metal-plastic and polypropylene water ducts is carried out using a solder coupling and a diffusion welding apparatus (soldering iron for polypropylene pipes), or a crimp fitting and a transitional combined coupling (polypropylene - internal metal thread).
Due to the simplicity and availability of methods for fixing polymer pipes, a plastic water supply system, in contrast to a metal one, is mounted much easier and faster, without the use of a rifling tool, physically heavy packages of threaded connections, or welding.