Often, even tap water is not particularly soft. And resources from autonomous sources (wells, wells) a priori leave much to be desired. Therefore, hard water and methods of softening it become the number one task for owners of suburban areas. There are many ways to deal with increased mineralization of liquids, and you can pick one for any budget.
Consequences of using hard water

The hardness of a drinking resource means a combination of chemical and physical properties of a liquid: the concentration of dissolved magnesium and calcium salts in it. The higher it is, the harder the water is. If magnesium and calcium carbonates are present in the liquid, this hardness is called carbonate (temporary). When boiled, dissolved salts are released from the liquid. Non-carbonate hardness is the presence of calcium and magnesium sulfates and chlorides in an aqueous medium. They cannot be overcome by heat treatment.
The main problems that the increased mineralization of water creates:
- dry skin and hair, peeling of the dermis, allergic reactions;
- low level of foaming during hygiene or household activities (bathing, washing, cleaning);
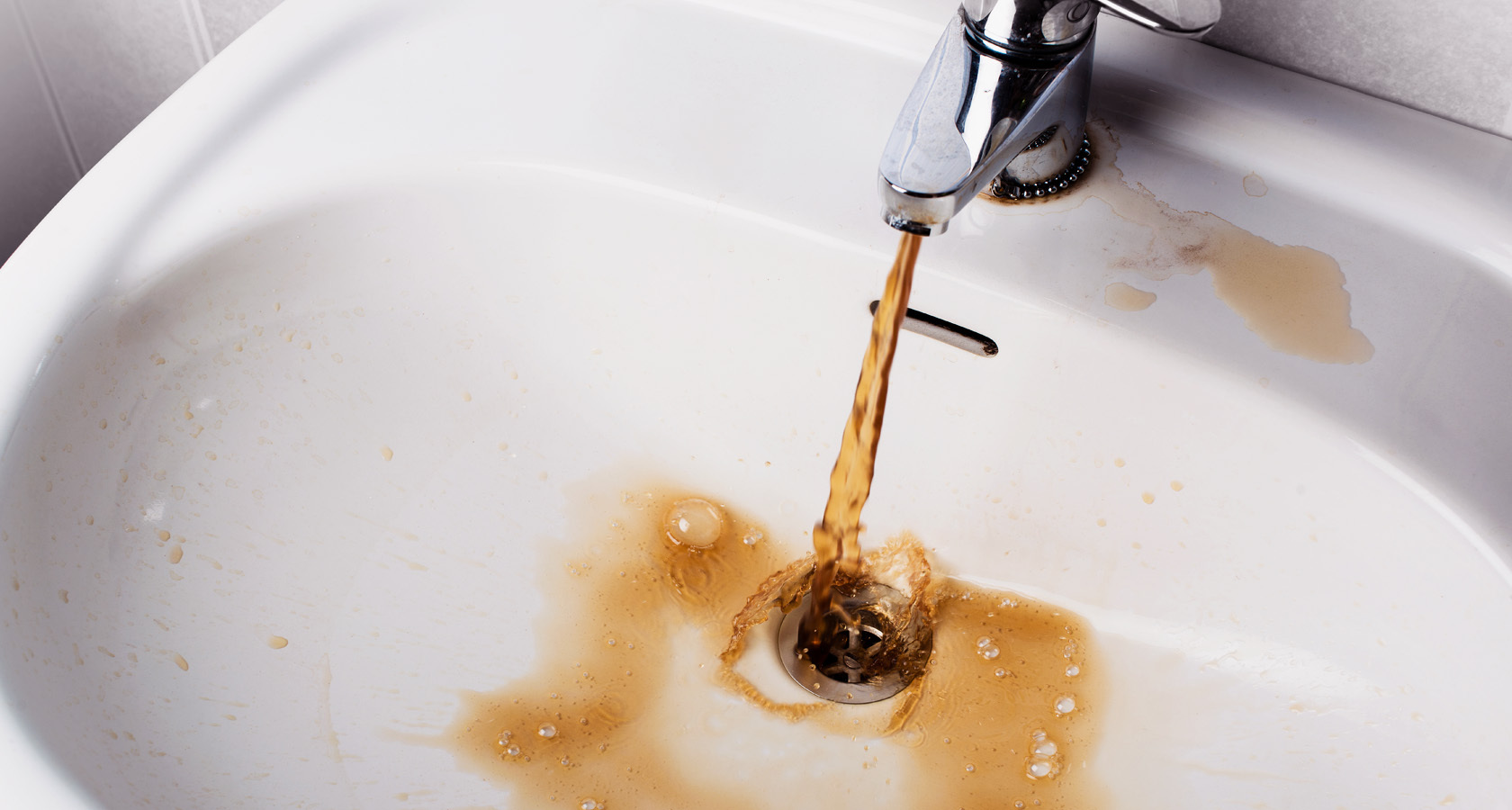
- the formation of thick layers of scale in household, heating, kitchen appliances (kettle, washing machine and dishwasher, boiler, heating pipes, etc.); due to the formed plaque, expensive equipment often breaks down;
- kidney problems with the constant use of highly mineralized water (urolithiasis);
- aerator and shower head clogged with limescale;
- the presence of white streaks on dark, washed laundry.
A whitish film on the surface of hot coffee or tea does not look very pleasant either.
Water hardness standards
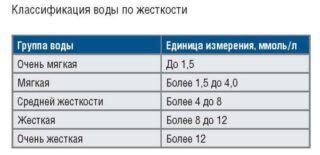
In total, three degrees of liquid salinity are classified:
- soft - up to 3 mg-eq / liter;
- average - 3-6 mg-eq / liter;
- hard - more than 6 mg-eq / liter.
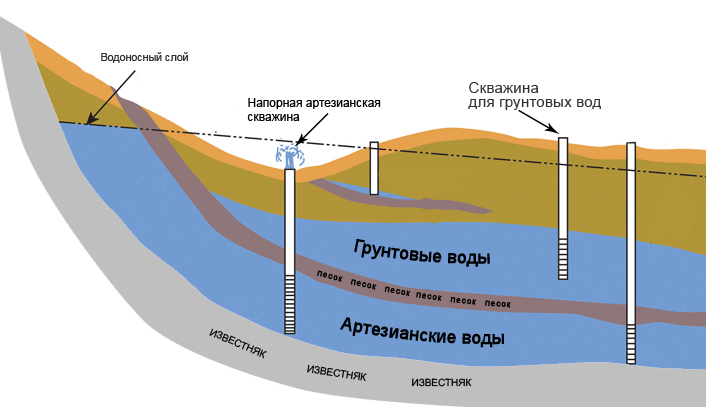
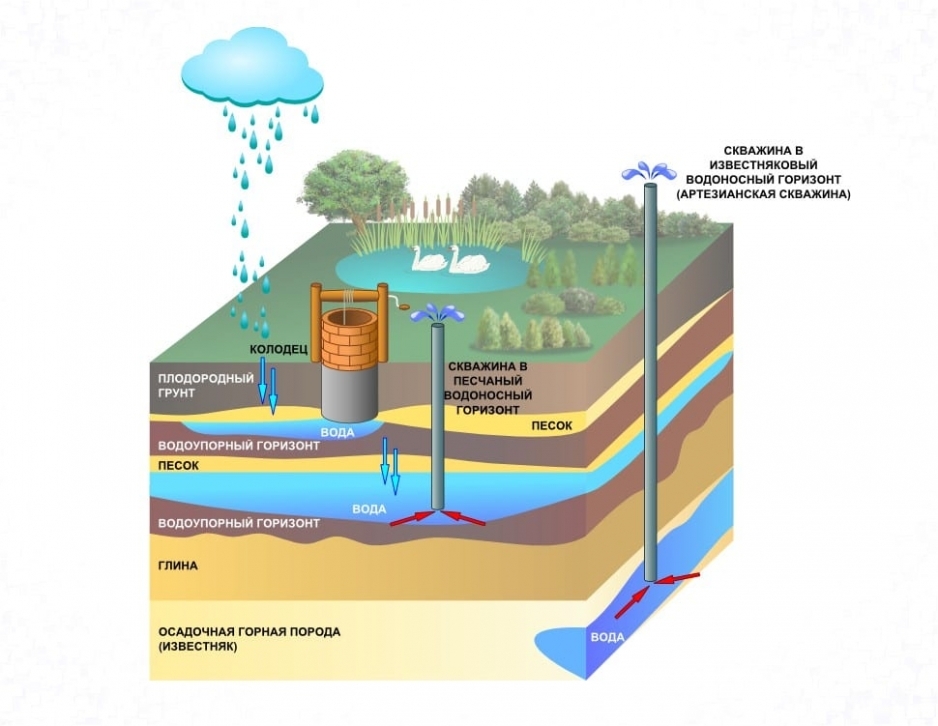
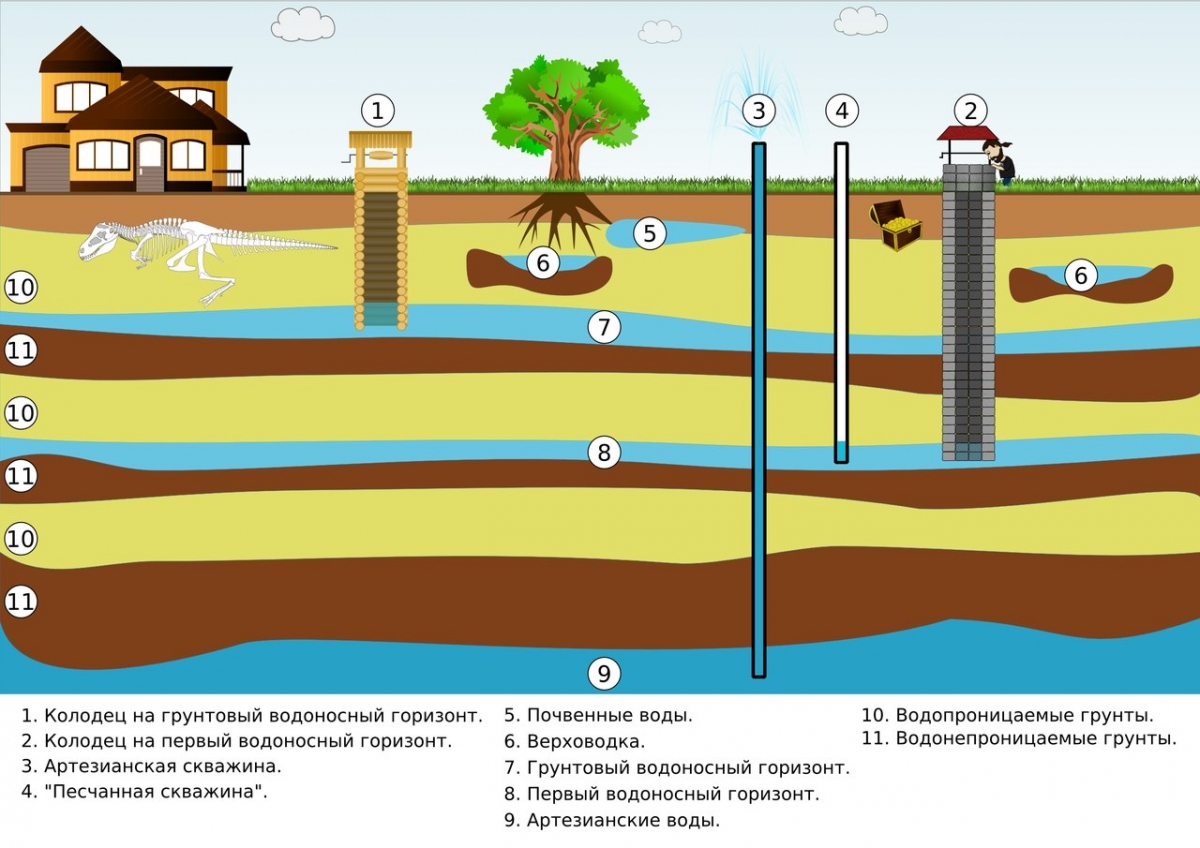
The reasons for the increased mineralization of water resources from a well or well are their communication with layers of limestone, dolomite, gypsum, etc.
Methods for determining the level of hardness
- install the correct programs for household appliances;
- buy the optimal cartridge for water softening;
- find the right dosage of emollients;
- provide optimal conditions for aquarium inhabitants;
- select a reliable and efficient filter system.
There are several ways to independently determine the level of mineralization of a liquid.
Accurate analysis
The collected sample is taken to the local SES. For the liquid, you need to pick up a clean polymer container. The volume of material for research is 1-2 liters. The sanitary and epidemiological station will not only determine the concentration of dissolved salts in the water, but also reveal the presence of pesticides, nitrates, hydrogen sulfide, manganese, iron, and organic matter. The analysis is especially good for the selection of the correct filtration unit or water softening system.
Using test strips
This is a quick way to determine the quality of a fluid. You can buy indicators at zoological stores or tea and coffee points of sale. A special reagent applied to the test strip turns to a specific color upon contact with dissolved minerals. The color intensity indicates the level of salt concentration in the water, that is, the degree of its hardness. The brighter the color, the more dissolved salts there are in the sample.
The highest quality test strips are those made in Europe.
Conducting a home experience
You will need warm distilled water and a bar of 72% laundry soap. From the equipment at hand you need to have a glass, a transparent liter container (you can use a can), electronic scales and a ruler.
They act in the following way during the experiment:
- Rub the soap on a fine grater and measure 1 gram. The finished mass is dipped into an empty glass.
- Distilled water is heated to 60-70 degrees and poured there. The soap should be completely dissolved.
- Distilled liquid is added to the glass at the rate for 72% soap - 7 cm, for 60% soap - 6 cm.
- The jar is loaded with 0.5 liters of tap (borehole, well) liquid.
- Distilled soap solution is slowly poured here and everything is stirred until foam forms, which indicates that the laundry soap has bound all the mineral salts.
- It remains to measure the height of the liquid below the foam and subtract it from the initial level in the jar. This will be the approximate concentration of dissolved minerals in the water.
Such an experience, although interesting, does not differ in increased accuracy.
The main methods of water softening
Thermal
Boiling is the easiest method and is suitable for a resource with variable mineralization. Calcium and magnesium bicarbonates decompose, forming calcium carbonate sediment and carbon dioxide. The good thing about this method is that it can be used at home without buying expensive equipment. But there are two drawbacks - large volumes of liquid cannot be processed, and lime scale will constantly form on the walls of kitchen appliances.
Another method of thermal action on hard water is freezing. Here, you can only use the liquid that remains on top after thawing.
Physical methods
- High pressure water flow through the membrane. As a result, only water molecules pass through a kind of barrier, but not particles of salts dissolved in it. The result is a practically distilled liquid. Reverse osmosis installations such as "Trickle", "Geyser", etc. work exactly according to this principle. The main advantage of the membrane method is the almost complete purification of the resource not only from salts, but also from other organic, inorganic impurities. The disadvantages of the method include the need for constant high pressure in the system (3-4 atm.), The impressive cost of softening equipment and additional mineralization of the liquid to make it usable. Otherwise, it is "dead" and brings harm rather than benefit to the body.
- Electromagnetic treatment. This method is considered relatively new. Electromagnetic waves of a specific frequency are passed through hard water. This leads to the fact that calcium and magnesium ions become suspended, lose the ability to precipitate. It is in this form that they are removed from the total volume of the liquid.
- Treatment of hard water with magnetic fields. Here, the principle of conversion of magnesium and calcium ions is similar to the effect on them of electromagnetic waves. The result is that dissolved impurities are suspended and removed through filters or into sedimentation tanks.
Any of the physical methods of water is ideal for industrial use, but costly for home use.
Chemical treatment
- lime;
- soda ash (baking soda) + salt;
- synthetic splitters;
- sodium chloride (table salt) + soda;
- table vinegar (this water is especially good for washing);
- lime + soda;
- special salt for softening liquids;
- drugs in tablets.
The principle of operation of the reagents used is the dissolution of all hard elements or their complete replacement with softer impurities.
The benefits of using reagents include:
- removal of all mineral impurities;
- prevention of scale on household equipment;
- neutralization of muddy stains on linen.
The disadvantages include:
- the inability to use the processed liquid for food (excluding soda and salt solutions);
- the need for knowledge and compliance with the dosage of reagents.
As a rule, in everyday life, simple salt and soda are used to soften the liquid. For one liter of water, 0.5 teaspoon of the reagent is enough.
To soften water in boilers of heating systems, special filters with polyphosphates are also used. These are peculiar white crystals that gradually dissolve as the liquid passes through them. Thus, they bind metal salts, making the environment softer. The polyphosphate softening method is suitable only for industrial, technical purposes. You cannot drink such water.
Ion exchange method
With this method, hard water passes through special loosened resins, which give up their ions and replace them with magnesium and calcium ions. More often, with a similar method, special installations are used. They are filled with resins such as AMBERJET 1200 Na, AMBERLITE SR 1L, etc.
The disadvantage of this method is that after a certain period of work, the bookmark must be disposed of in accordance with sanitary standards. The advantages of the method include the ability to process large volumes of liquid, high quality softening. More often this is an industrial technological process than a household one.
The liquid driven through the ion exchange plant is unsuitable for consumption.
For the home, it is advisable to use combined methods of softening, deferrization of the water resource, based on the use of special versatile filters. They are selected according to the type of pollution and the level of mineralization.