Water management is one of the industries. The main task is to keep records, study and plan the integrated use of water resources, protect underground and surface sources from pollution, transport them to the end consumer, thus providing all sectors of the national economy with the necessary volumes of water and proper quality. By the nature of their use, the branches of the national economy are divided into water users and water consumers.
Who are water consumers and water users

Water consumers are industrial enterprises, utilities and agriculture. As a rule, they irretrievably take water from sources (reservoirs, rivers, storage facilities, etc.). Water users, in turn, use not the source itself, but only a humid environment - fisheries, water transport, hydropower, etc.
Water consumers and water users can be industrial enterprises and organizations, citizens of their country, as well as foreign individuals and legal entities, stateless persons who use the water resource for their life.
Classification
Water users and water consumers are classified into several types, each of which has individual characteristics.
Types of water use
- the impact of consumers on water bodies and the quality of resources;
- purposes of water use;
- methods of using a liquid medium;
- technical conditions;
- the nature of the use of the water resource.
Depending on the goals, water users are divided into communal and food, household, industrial (without use in heat power engineering), as well as watering and irrigation, territorial distribution.
The primary water users are the owners of the water intake equipment and related structures. Secondary or subscribers are those organizations or people that do not have their own equipment and structures, they are provided with the required volume of water resource by primary users, then they discharge waste liquids into the sewer mains on conditions that were previously agreed between the parties.
According to the terms of transportation of the resource for use, it is divided into separate and joint.
By the nature of the use of the liquid as a substance with certain characteristics:
- mass application;
- water as a habitat;
- energy potential.
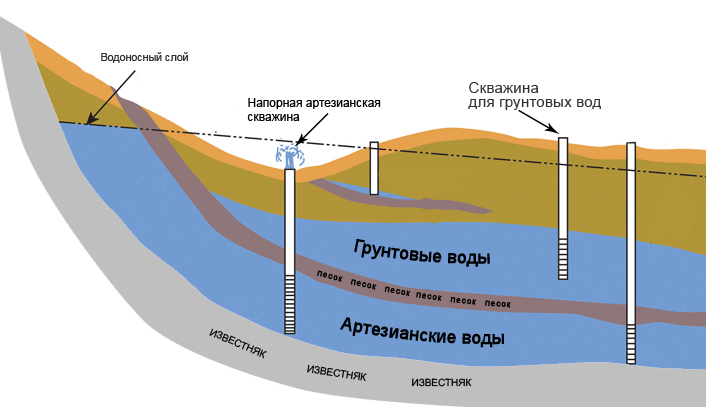
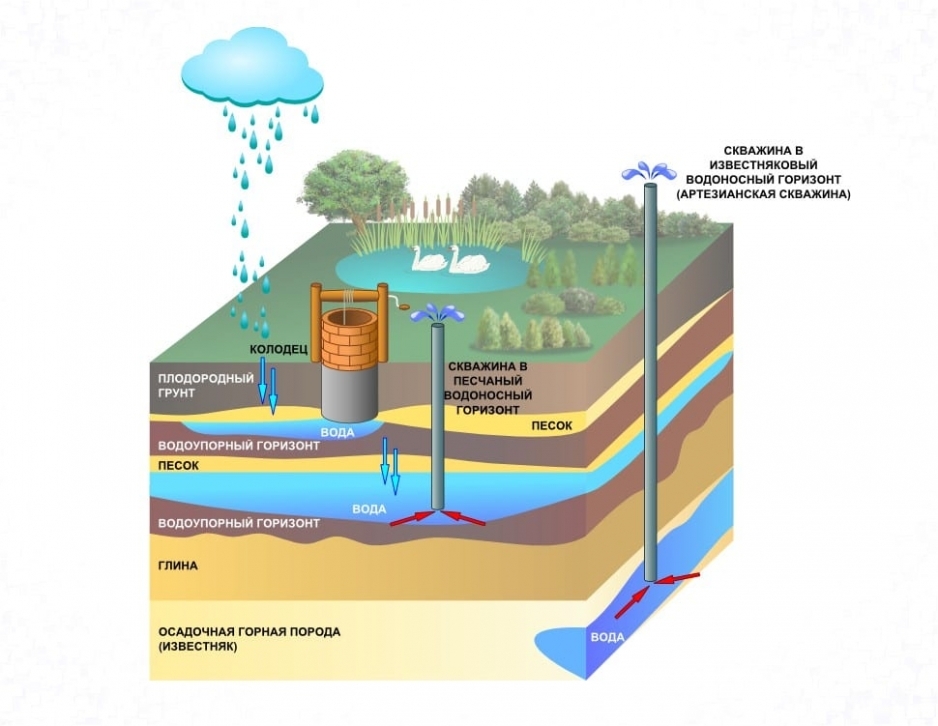
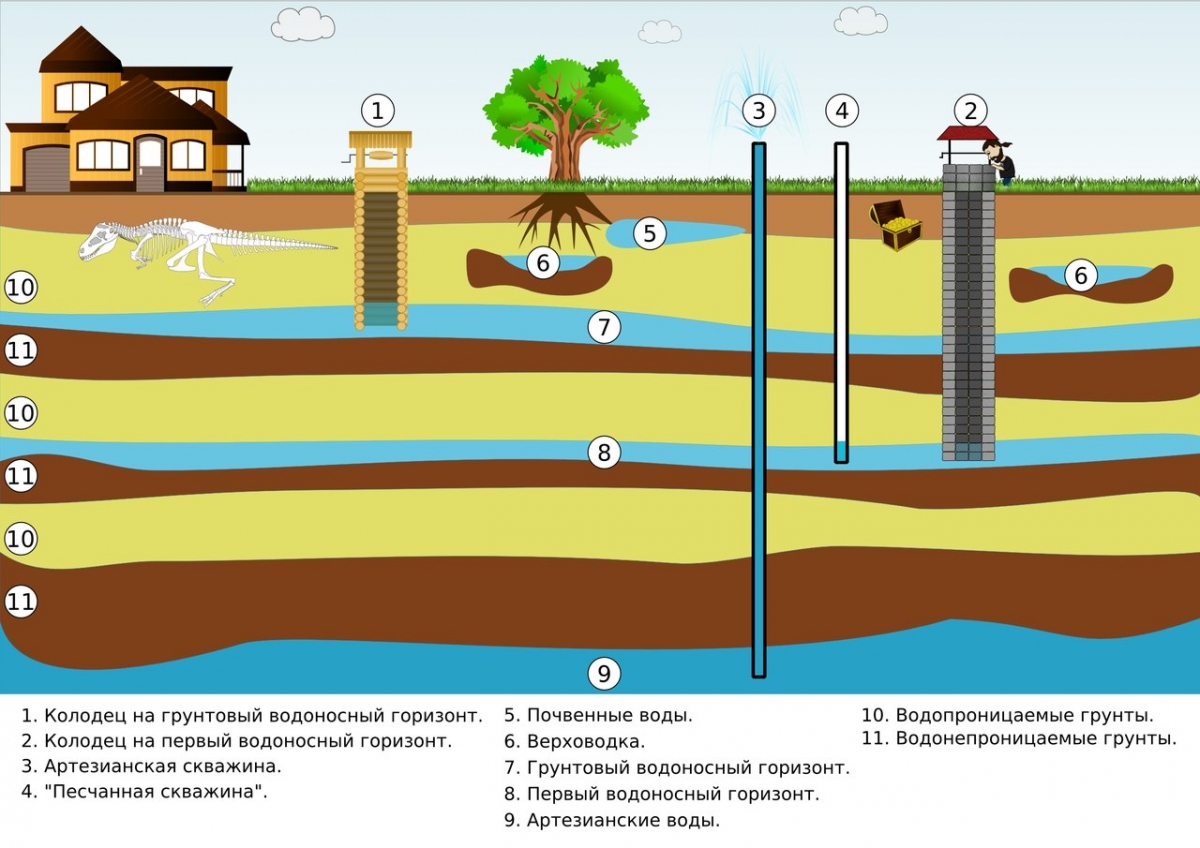
Objects of natural resource use are divided into marine, inland and underground. According to technical conditions, water use is subdivided into special and general.
Main types of water consumers
- household and drinking needs of the population;
- meeting the production needs of industrial enterprises;
- work of fountains, irrigation of green spaces, washing of settlements.
- extinguishing fires.
All types, with the exception of the latter, provide for a continuous supply of water, the volumes of consumption vary depending on the season. Fighting fires involves the occasional use of water, the intake, as a rule, comes from reserve tanks.
The water supply system must satisfy all the needs of the end user (consumer).A large number of objects are a collection of consumers of water resources of different categories.
The main differences
Water intake in large volumes blurs the boundaries between these concepts. For example, during the construction of energy reservoirs, a significant part of the resource is lost for filtration and evaporation. A similar state of affairs is observed when using large volumes of liquid for cooling equipment of nuclear and thermal power plants. In this regard, the industry began to actively combine these two concepts into one - water users. The most significant in water use is water consumption and wastewater disposal.
Wastewater disposal involves the discharge of wastewater - the removal of contaminated liquid far beyond the boundaries of the settlement or other places of use. The total volume of wastewater disposal includes all types of waste liquids that are discharged into endless depressions, underground horizons, and are also transported to filtering stations for purification and reuse.