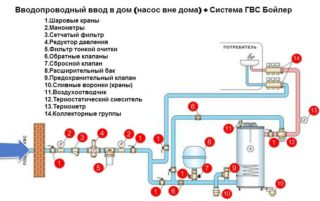
The inlet is the part of the pipeline that connects the external water supply to the water metering unit in the house or in the central heating point. Knowledge of the rules for arranging the entrance area is necessary for the functional integration of the elements of the water supply network located inside and outside the building.
Device and diagram of water supply network inputs

The inlet section connects the external water supply network from the connection point to the water metering unit or overlapping element. The complex also includes the sealing of the passage of pipes into the house.
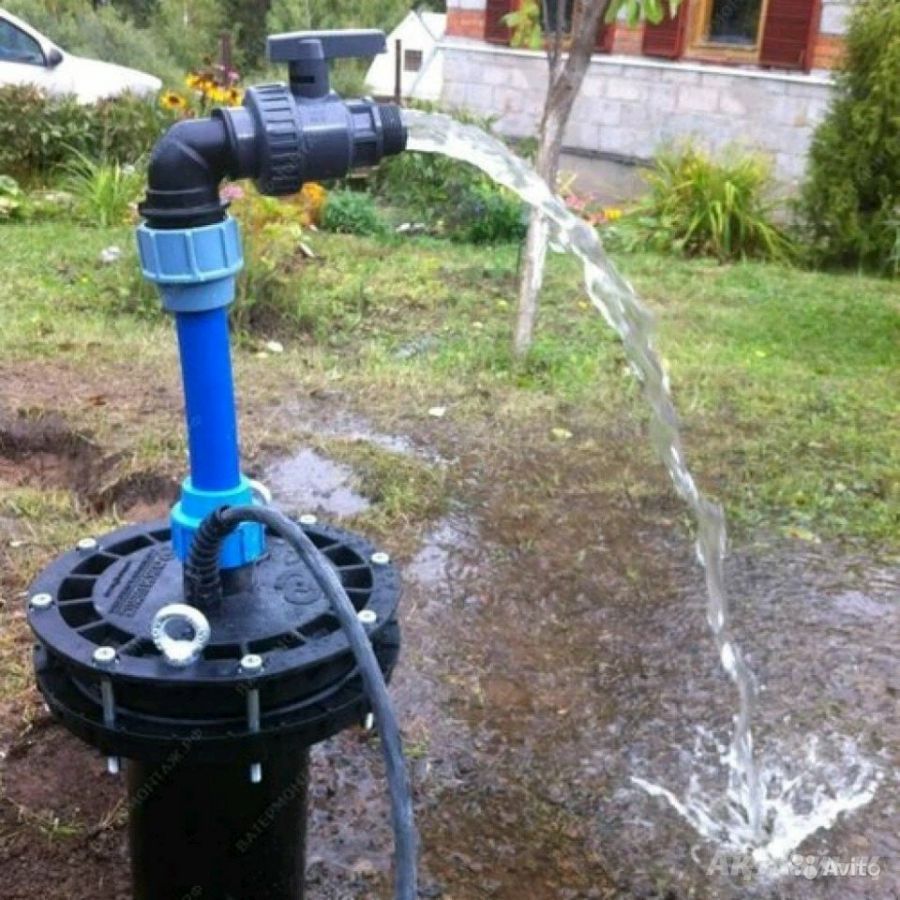
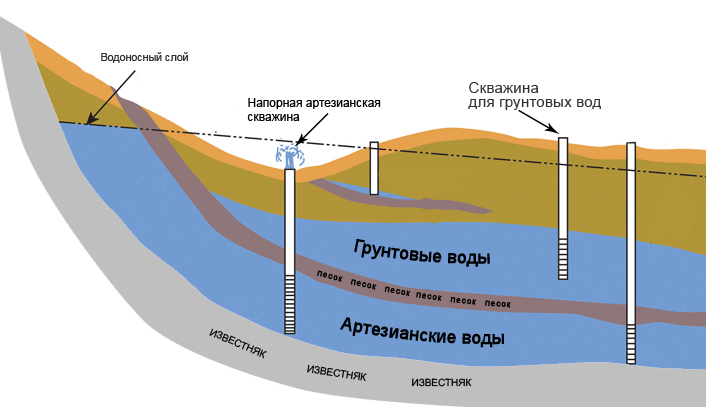
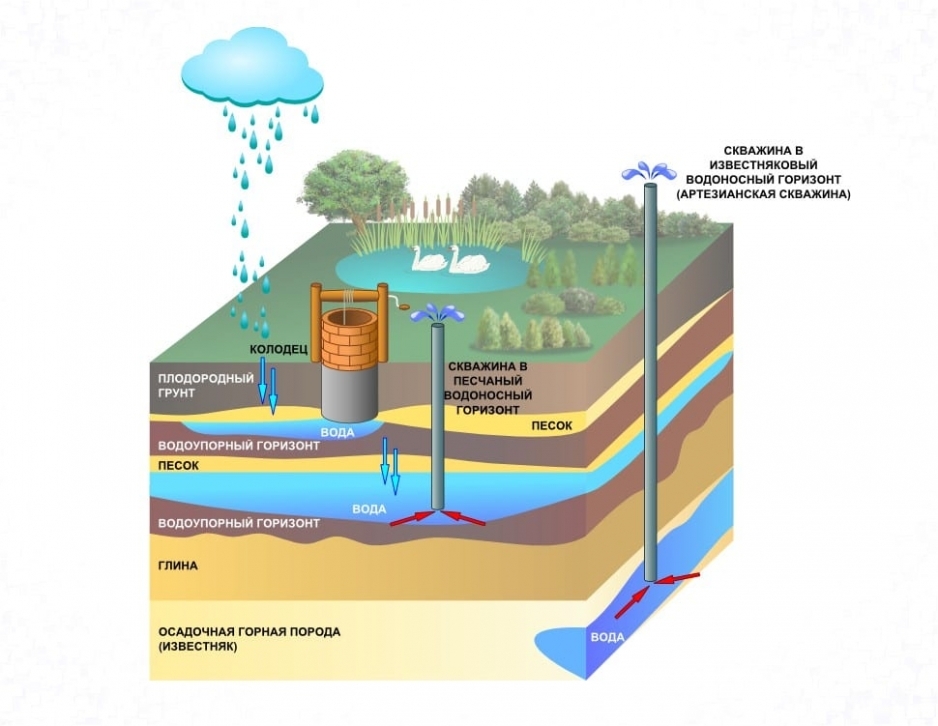
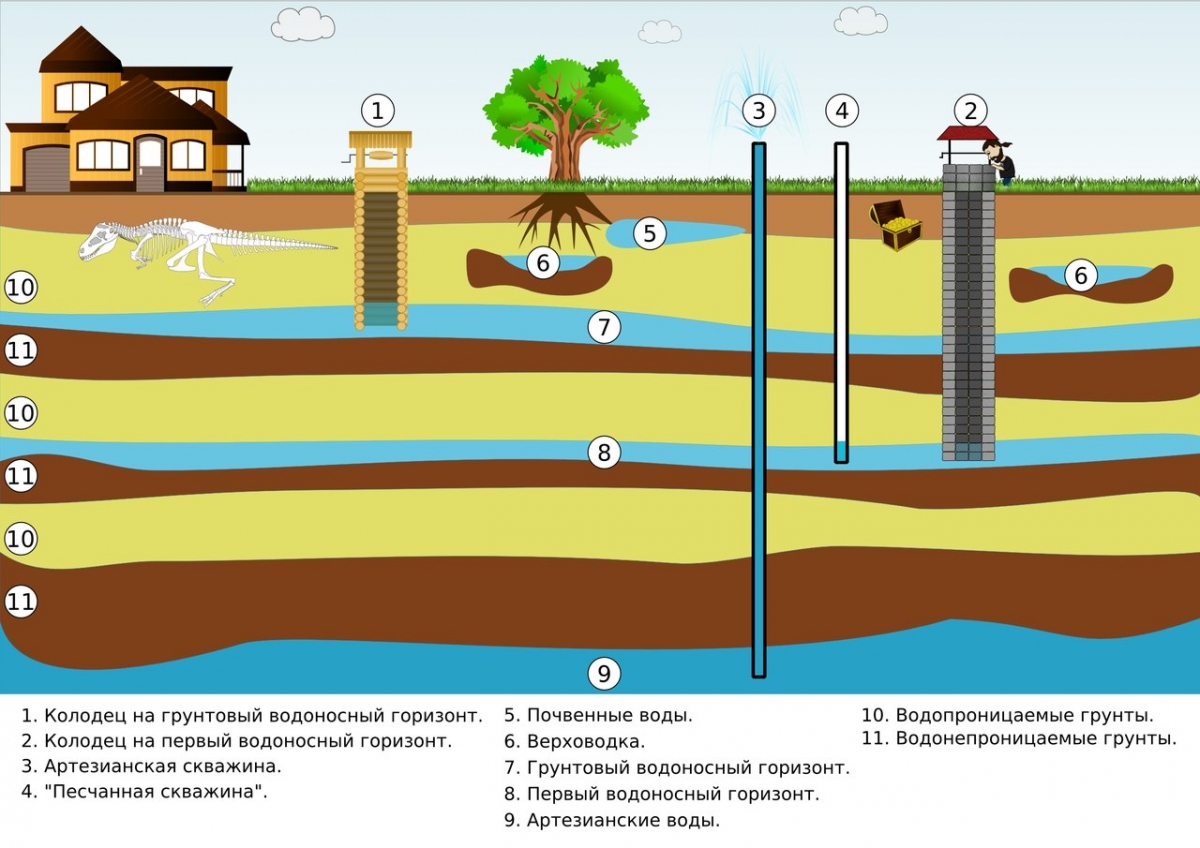
There are two types of introduction of the water supply main into the building: from the central network or from a local water source. The decentralized method is used when the water supply systems are located far from buildings. The connection is made from a well or a well. In this way, private houses are usually powered, they are equipped with a single input.
In high-rise buildings, 400 or fewer apartments have each water supply connection. The number of inlet sections depends on the mode of providing moisture to consumers:
| Number of inputs | Installability |
| One | In buildings, inside which there are dead-end highways and less than 12 fire hydrants. |
| Two and more | Inside buildings there are more than 16 floors, as well as in buildings equipped with a zone plumbing system and where more than a dozen fire hydrants are provided. |
The total number of inputs is determined by the selected water supply scheme. In residential and public buildings of standard construction, there is usually one lead-in node.
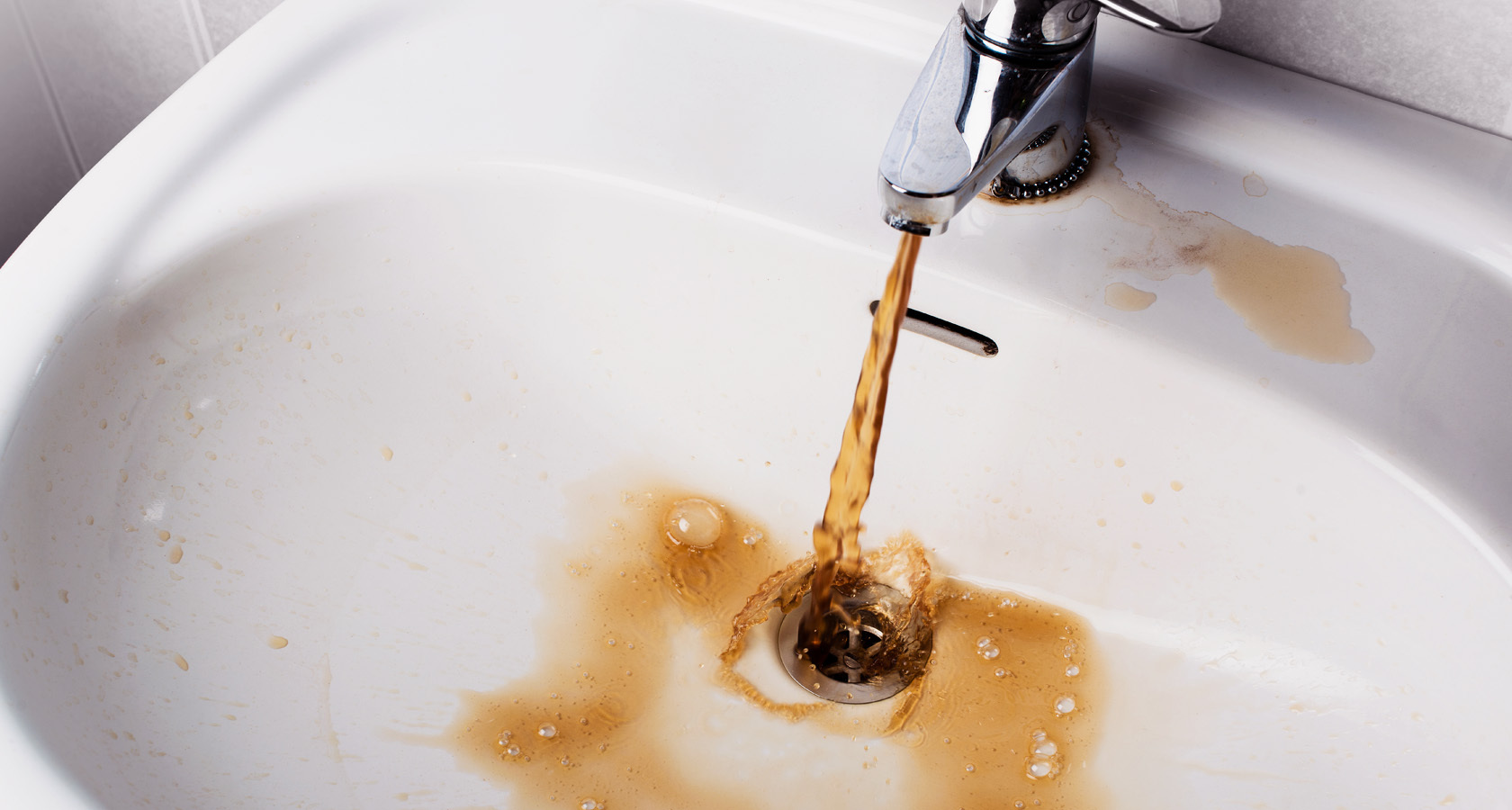
At the junction of the input and the outer part of the water supply network, a well tank with a diameter of at least 70 cm is equipped to accommodate shut-off valves. This can be a valve or gate valve that allows you to shut off the water flow at any time.
When installing two or more bushings, they are connected to different sections of the outer ring line, mounting a dividing valve on it. If pressure equipment is additionally installed, which increases the pressure inside the water supply network, the inputs are arranged in front of the pumps. In this case, locking elements are mounted on the connecting element. They will provide moisture to all pumping equipment. The inlets are not connected if each of them is equipped with an independent pressure station.
If the house is connected to a centralized network, the installation of a water meter is mandatory.
Connecting water inlets
- directly to the tees, crosses or plugged holes left during the construction of the city highway;
- connecting the pipe to the mainline by welding or cutting in a tee;
- by means of a saddle.
In the latter case, a cast-iron shaped part is used, fixing it to the water supply with a clamp on a rubber gasket. The saddle is used when it is not possible to shut off the external water supply. Locking fittings are fixed on it - a straight-through valve or a gate valve - by means of a threaded or flange connection. To drill a hole in the pipe, a drilling device is attached to the closure element.
A valve or gate valve is also installed at the point of connection of an input with a cross section of more than 50 mm to an external plumbing system. Introductory nodes are equipped with stops in the sections of turns along the vertical or horizontal plane.
When installing several bushings on the internal line with measuring devices connected by pipe sections, it is required to provide for the installation of check valves
Pipe materials and sizes
For the arrangement of bushings with a cross section of 50 mm or more, cast iron pipes are mainly chosen, with a smaller diameter - pipelines made of steel, galvanized or polymers. Steel products without zinc coating with bitumen insulation against rust are used when the pressure in the main line is more than 1 MPa and the cross-section of the bushings is more than 50 mm.
When selecting pipe sections according to the size of the section, they are repelled by two criteria: the speed of the water flow, as well as the total length of the water main. The first indicator is usually standard: water moves at a speed of about two meters per second. The second varies depending on the area of the building and the remoteness of plumbing fixtures. For example, with an estimated length of a water supply system of less than ten meters, pipe sections with a cross section of 20 mm, from 10 to 30 m - 25 mm and more than 30 m - 32 mm will be enough.
Building regulations
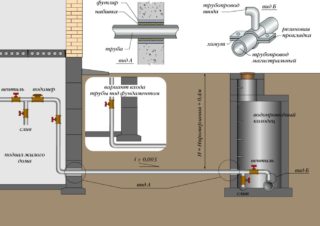
The node for entering the water supply into the building is equipped under a non-residential premises, for example, under a staircase, since a station of two pumps can be located nearby: a working and a spare. Finding pumping equipment under residential premises is prohibited by Building Codes and Regulations 2.04.01-85.
The laying of the input pipeline is carried out at a minimum distance at an angle of 90 degrees to the wall of the house and with an inclination of 0.005 to the city-wide highway. This will allow excess moisture to drain away.
The entrance section at the point of passage through the wall or foundation of the building must be protected from mechanical damage. For this, pipe sections in dry soils are placed in cases made of steel sleeves with the annular gap sealed with tarred fiber and crushed clay, and on the outside with cement mortar for sealing. In soils saturated with moisture, ribbed pipes are used for arranging inputs passing through the walls and foundation foundations, and when subsoil sources are close, glands are used or sealed with cement, concrete mixture.
The size of the opening for the inlet in the wall of the foundation or basement of the building must be 40 mm larger than the cross-section of the inlet pipe.
The minimum distances in the horizontal direction from the pipes of the inputs to other underground utilities are established by building codes:
- to the heating main - 1.5 m;
- to the sewer main with a cross-section of the input up to 20 cm - 1.5 m, more than 20 cm - 3 m;
- to low pressure gas pipeline networks - 1 m, medium pressure - 1.5 m;
- to electric cables and telephone wires - 0.75–1.0 m.
At the intersection with the sewage main, the water supply network is laid 40 cm higher. The entrance section, ideally, is also located above the sewer pipes. If the water supply input can be arranged only below the wastewater outlet, the distance criteria listed above must be increased by the difference in the depth indicators of pipelines. At the same time, pipes made of steel are necessarily used, placed in a case with an overhang in both directions up to a meter.
The depth of the inlet of the water main depends on how the external water supply pipeline passes. It is important that the entry plots are located below the soil freezing level. The minimum depth indicator for laying is a meter, but only if the ground temperature at this mark is above zero. Be sure to keep in mind that to ensure free drainage from the system, the input is installed with a slope of 0.005 towards the external water supply network.
The arrangement of the lead-in section should be foreseen even before the construction of the building. If difficulties arose during the self-creation of a diagram of this node, you need to contact the design office.